Mirena IUD
- Introduction to Mirena IUD
- Composition of Mirena IUD
- How Mirena IUD Works
- Uses of Mirena IUD
- Off-Label Uses of Mirena IUD
- Mirena IUD dosage and AdministrationÂ
- Storage and Handling of Mirena IUD
- Side Effects of Mirena IUD
- Common Side Effects of Mirena IUD
- Warnings and Precautions for Mirena IUD Use
- Contraindications of Mirena IUD
- Interactions with Medications or Treatments
- Administration Guidelines for Specific Populations
- Overdosage of Mirena IUD
- Important Precautions for Patients and Providers
- Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Introduction to Mirena IUD
Overview of Mirena IUD
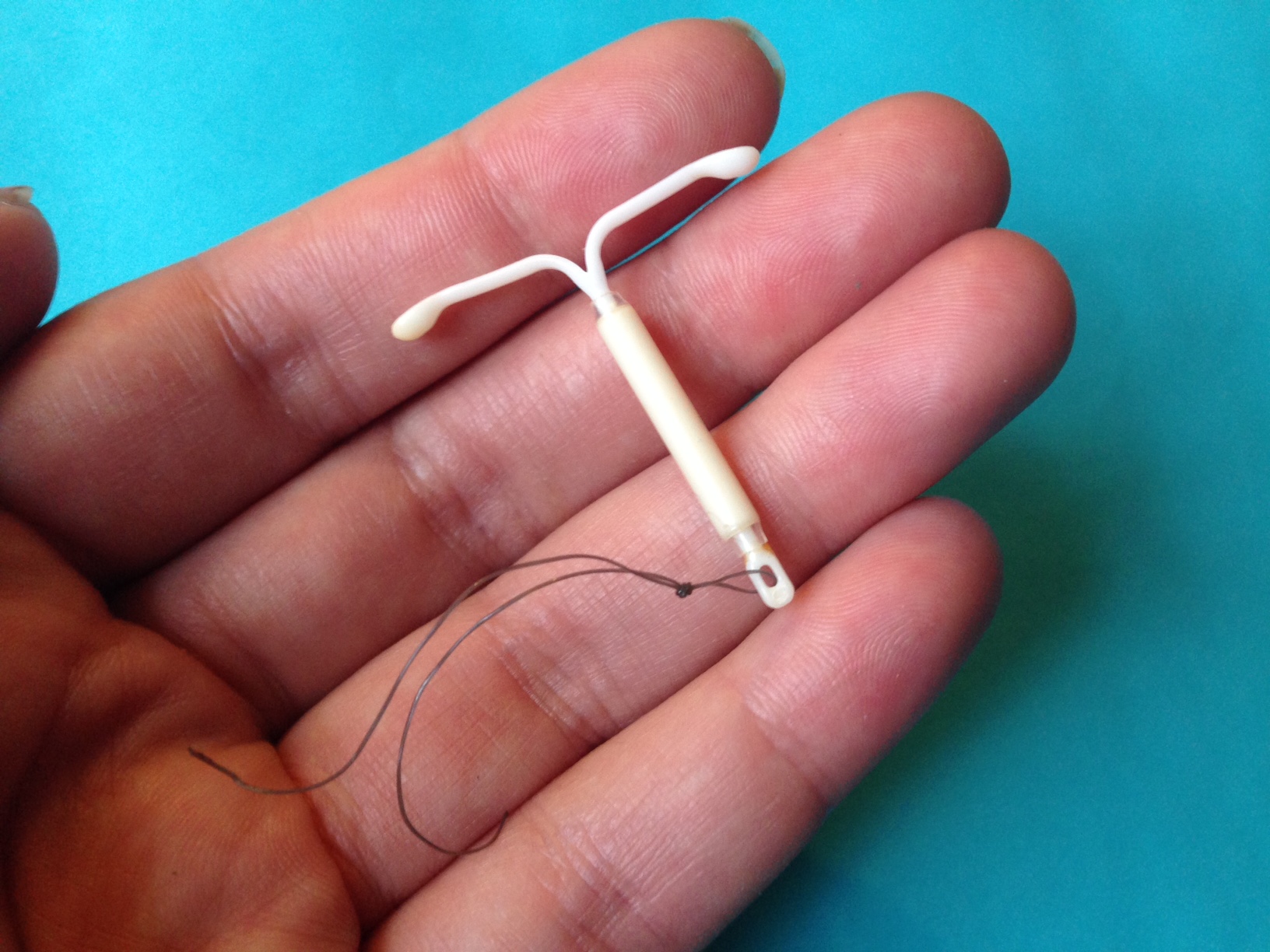
The Mirena IUD is a device that uses hormones to prevent pregnancy and provide benefits over an extended period of time. It's a T-shaped device that releases levonorgestrel, a hormone that delivers reliable birth control for up to five years. Because of its effectiveness compared to birth control methods, it has gained the trust of countless individuals seeking reliable contraception options.
Brief History and Development
Developed in the late 20th century, the Mirena IUD emerged as a revolutionary advancement in reproductive health. Approved by regulatory authorities in the early 2000s, its safety and efficacy have been validated through extensive clinical trials and user experiences.
Popularity and Mirena IUD effectiveness
Mirena is a choice, among women worldwide for its convenience and effectiveness as an IUD option. Studies show that its usage has been increasing by 15 percent each year among women between the ages of 25 and 40. This trend highlights Mirena's reputation for being safe and reliable.
Composition of Mirena IUD
Material and Structure of the Device
The Mirena intrauterine device is made of flexible plastic to provide comfort when being inserted and worn in the bodys cavity shaped like a T to fit perfectly inside the uterus with strings that reach into the canal for simple removal.
Hormonal Composition and Active Ingredients
The product includes 52 milligrams of levonorgestrel that is slowly released over time to minimize absorption and decrease the chances of side effects occurring.
Mechanism of Hormone Release
The use of levonorgestrel in a silicone reservoir ensures a reliable release mechanism for the medication's effectiveness. The targeted impact is mainly on the uterus, which improves its safety characteristics in comparison to contraceptives.
Copper IUD vs Mirena
Copper does not have hormones in it; in contrast, Mirena has levonorgestrel hormone in it. Copper IUD is effective for preventing pregnancy for a decade, while Mirena works for up to eight years.
Liletta iud vs mirena
Both Mirena and Liletta are types of devices (referred to as IUDs) designed to prevent pregnancy effectively with comparable side effects and advantages in their use; their insertion procedures also share similarities in the process involved.
Kyleena IUD vs mirena
Kyleena has 19.5 milligrams of levonorgestrel in it compared to Mirena which contains 52 milligrams. Kyleena can be used for up to five years whereas Mirena is effective for up to eight years.
Paragard iud vs mirena
ParaGardis is an IUD without hormones, crafted from copper, which can stop pregnancy for a decade in women who use it, while Mirena is an IUD constructed from plastic with a reservoir of the hormone levonorgestrel providing protection for up to 8 years.
How Mirena IUD Works
Mode of Action in Contraception
The Mirena contraceptive functions by thickening the mucus to form a barrier that inhibits sperm from penetrating. This method of action significantly decreases the chances of fertilization and boasts a 99 percent success rate in preventing pregnancy.
Hormonal Effects on the Uterine Lining and Cervical Mucus
Mirena works by decreasing the thickness of the lining to lower the likelihood of embryo attachment and by thickening mucus to slow down sperm movement and improve its contraceptive effectiveness.
Impact on Ovulation
While Mirenas main function is not to suppress ovulation it may still reduce ovulation, in women to some extent This additional impact adds to its effectiveness, as a contraceptive method overall.
Uses of Mirena IUD
Contraception: Primary Use
Mirena is a trusted choice for women seeking effective and reversible contraception. Its low-maintenance nature appeals to individuals looking for hassle-free family planning options.
Treatment of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (HMB)
Approved for managing heavy menstrual bleeding, Mirena significantly reduces blood loss and improves quality of life for women with menorrhagia. It is often considered a first-line treatment.
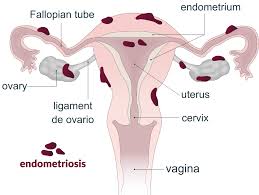
Mirena IUD for endometriosis
Role in Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Sometimes, Mirena is combined with estrogen therapy to help prevent hyperplasia, showcasing its flexibility in treating gynecological issues beyond its approved use.
Off-Label Uses of Mirena IUD
Use in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Management
Prevention of Uterine Hyperplasia in Postmenopausal Women
Management of Dysmenorrhea
Potential Use in Endometrial Cancer Prevention
Recent findings indicate that Mirena could potentially lower the chances of developing cancer among individuals at risk with ongoing studies delving further into this encouraging possibility.
Mirena IUD dosage and Administration
Recommended Patient Profile
For women looking for a form of birth control over a period of time or those dealing with heavy menstrual periods or needing additional treatment for certain gynecological issues, Mirena could be a suitable option.
Steps of Insertion Procedure
- Preparation: Patient counseling and pelvic examination.
- Insertion: Placement within the uterine cavity by a trained provider.
- Post-procedure: Immediate monitoring for adverse reactions.
Removal Guidelines and Replacement Timing
Mirena should be replaced after five years or earlier if desired. Removal is a simple outpatient procedure, typically completed within minutes.
Mirena IUD strings
The Mirena IUD comes with a pair of strings that extend from the part of the T shaped device passing through the cervix and reaching into the vaginal canal.
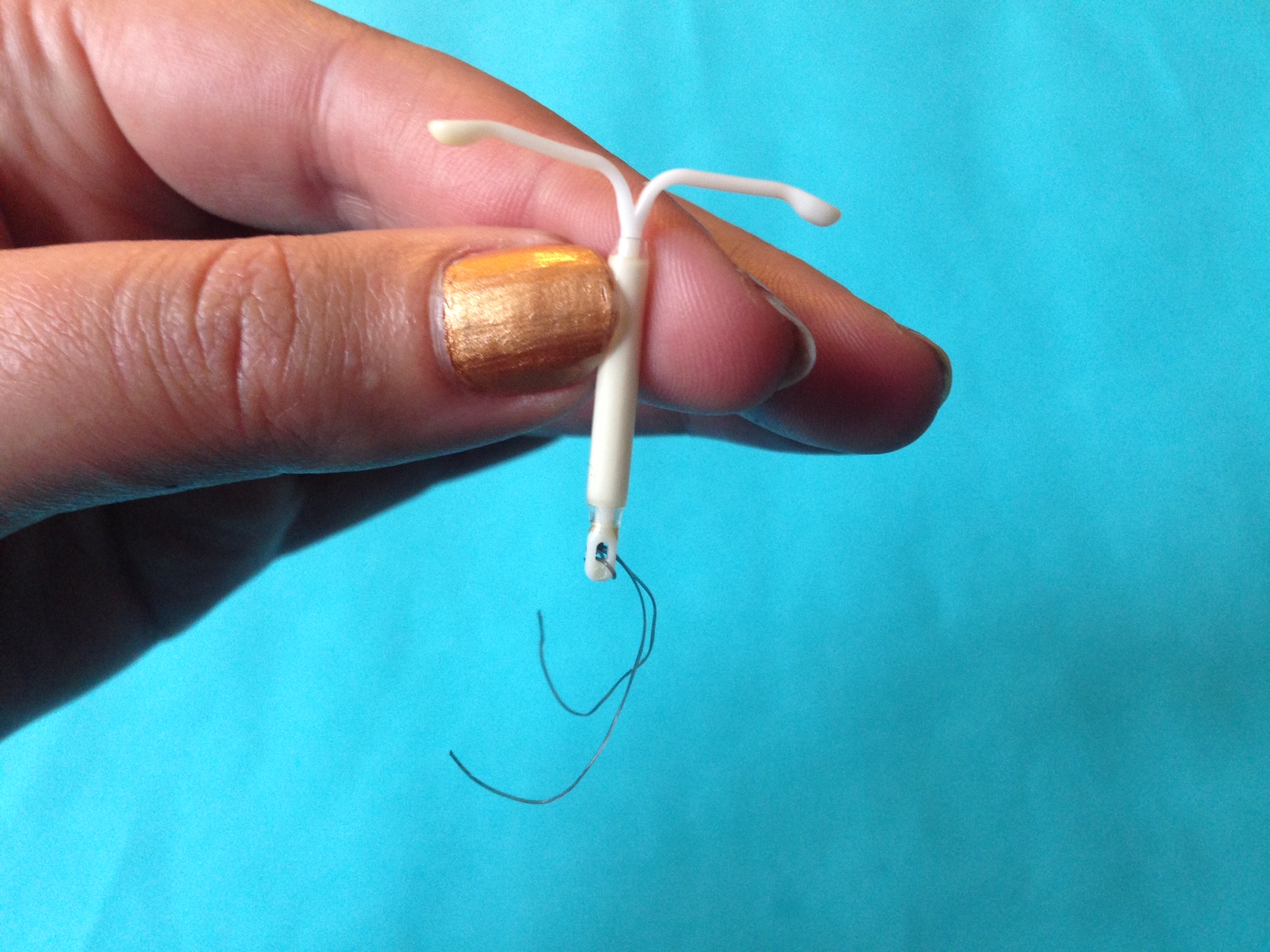

Storage and Handling of Mirena IUD
Proper Storage Conditions
Remember to store Mirena in a dry spot that is shielded from sunlight to maintain the quality of the device and its parts.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Remember to keep everything sterile when handling and inserting to avoid infections. Healthcare professionals should adhere to established procedures for well-being.
Safe Disposal Guidelines
Dispose of used devices in accordance with waste regulations to avoid contamination.
Side Effects of Mirena IUD
Common Side Effects: Overview and Frequency
- Mirena IUD spotting
- Mild cramping during and after insertion
- Mirena IUD mood swings
- Mirena IUD acne
- Mirena IUD hot flashes
Rare but Serious Side Effects
While uncommon, complications such as uterine perforation or pelvic inflammatory disease can occur. Prompt medical attention is essential in such cases.
Long-Term Effects and Complications
Most users tolerate Mirena well; however, rare cases of device expulsion or hormonal imbalance require evaluation. Regular follow-ups help mitigate risks.
Mirena iud neurological side effects
- Intracranial hypertension (ICH), a condition that raises pressure in the brain and nervous system, can result in papilledema. Swelling of the optic disc leads to potential blindness.
- Post traumatic condition (PTC). Symptoms of PTC consist of headaches, along with vomiting and nausea, often coupled with ringing in the ears; if not addressed promptly, blindness may ensue.
Common Side Effects of Mirena IUD
Spotting and Irregular Bleeding Patterns
Irregular bleeding is a noted side effect of using the Mirena IUD for individuals during the first few months of use due to hormonal adjustments in the body system, causing spotting between periods on occasion as it adapts to the changes in hormones released by the IUD over time which typically resolves within a span of 3 to 6 months resulting in either lighter menstrual flows or complete absence of periods altogether, for some users.
Hormonal Effects: Acne, Mood Changes, and Breast Tenderness
The hormonal element in Mirena, known as levonorgestrel, might lead to effects for some individuals using it, experiencing outbreaks of acne or mild shifts in mood and moments of irritability being reported by users as well as occasional breast tenderness which typically subsides over time with consistent use.
Mirena IUD lower back pain
Experiencing discomfort or mild pain during or after insertion is common for individuals and usually improves within a few days on its own accord. However if the pain persists or becomes severe it is advisable to seek advice to rule out any issues such, as incorrect placement or perforation.

Mirena IUD yeast infections
This research validates the theory that using IUDs increases the likelihood of colonization and infection by Candida albicans and other strains.
Warnings and Precautions for Mirena IUD Use
Risks Associated with Improper Placement
Correct placement of the Mirena IUD is critical for its efficacy and safety. Improper insertion may lead to uterine perforation or expulsion. Users should immediately report severe pain, heavy bleeding, or any signs of device displacement.
Mirena IUD moved out of place symptoms
- Pain: Feel pain or soreness in your lower abdomen
- Bleeding: Abnormal vaginal bleeding or bleeding when you're not on your period
- Discharge: Unusual vaginal discharge
- IUD strings: Misplaced IUD strings
- Partner can feel it: Your partner may be able to feel the IUD during sexual intercourse
Expired mirena IUD symptoms
Changes in the cycle and shifting of the IUD position, can result from imbalances when using an expired IUD and may cause discomfort or infection risks to increase slightly higher chances of pelvic inflammatory disease onset, a severe infection with potential long-term harm to the reproductive system.
Signs of IUD infection Mirena
- Experiencing discomfort in the abdomen
- vaginal discharge that may have an unpleasant smell
- pain during urination
- discomfort during sexual intercourse
- fever
Warnings for Individuals with Pre-Existing Conditions
Women who have experienced disease in the past or have had recurring urinary tract infections or uterine abnormalities should be careful when considering this option and should undergo a comprehensive medical assessment before moving forward with the insertion process.
Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Healthcare professionals usually advise scheduling a follow-up appointment within 4 to 5 weeks after the device's placed to ensure it stays in the position and works effectively, with yearly checkups recommended thereafter for maintenance purposes.
Mirena IUD discharge
It is common to have bleeding or spotting, like a dark brown discharge, in the initial 3 to 6 months after having a Mirena IUD inserted.
Mirena IUD and menopause
The Mirena IUD is a device that does not impact the start of menopause but can assist in managing certain symptoms associated with menopause and perimenopause and can be included as part of hormone replacement therapy ( HRT ).
Contraindications of Mirena IUD
Absolute Contraindications
- Pregnancy or suspected pregnancy.
- Active pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Known or suspected uterine or cervical malignancy.
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding.

Relative Contraindications Requiring Medical Discretion
The individualized evaluation may be necessary for conditions like a pregnancy history or significant liver disease and clotting disorders to determine appropriate actions for each patient after considering both risks and benefits carefully.
Mirena IUD breast cancer
Mirena is a type of intrauterine device (IUD) that contains the hormone levonorgestrel, a type of progestin. While hormonal IUDs like Mirena can slightly increase the risk of breast cancer, the overall benefits of hormonal contraception outweigh the risks
Interactions with Medications or Treatments
Medications That May Affect Hormonal Efficacy
Some types of medications such, as rifampin, carbamazepine and phenhytoin can lessen the impact of Mirenas part Patients should let their healthcare providers know about all the medicines they are taking simultaneously.
Interactions with Antibiotics or Anticoagulants
Most antibiotics typically don't interfere with Mirena; however, medications intended for tuberculosis or fungal infections may have an impact. Additionally blood thinners could heighten the chances of bleeding issues during or post insertion.
Impact on Other Medical Devices
Interactions with devices placed in the uterus or surgical implants are not frequently encountered; It is important to keep them in mind when they are used together simultaneously. Paying attention to the spacing and ensuring compatibility is crucial, in situations.
Administration Guidelines for Specific Populations
Elderly Patients: Considerations and Recommendations
Women who are past their reproductive years are not often given Mirena as a prescription; in certain situations, like postmenopausal hormone therapy it might be recommended under careful medical supervision.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety and Usage Guidelines
Avoid using Mirena as it may lead to results; however, it is generally considered safe for postpartum contraception in breastfeeding women due to its low hormone levels that have little effect on milk production.
Children and Adolescents: Age-Related Restrictions and Indications
It is generally advised not to use Mirena before a woman's first menstrual period begins (menarche). However, for teenagers dealing with issues, like periods or endometriosis that don't improve with treatments it might be a consideration.
Overdosage of Mirena IUD
Possibility and Symptoms of Overdosage
Overdosing on Mirena is very improbable because of its regulated hormonal release mechanism; nevertheless, experiencing symptoms like nausea, headaches, or hormonal imbalances due to exposure to levonorgestrel is a possibility.
Recommended Medical Interventions
If overdosage is suspected, removal of the device is typically sufficient to resolve symptoms. Supportive care may be provided as needed to address specific side effects.
Important Precautions for Patients and Providers
Ensuring Correct Placement During Insertion
Proper training and experience are vital for healthcare providers performing insertions. Ultrasound guidance may be used in cases of anatomical challenges.
Recognizing Signs of Displacement or Perforation
Patients need to keep an eye out for bleeding occurrences and severe pelvic discomfort. If the device is pushed out of place. Healthcare providers should make sure to inform individuals about these flags during their first appointments.
Post-Insertion Care and Monitoring
Regular checkups are essential to keep the device running smoothly and efficiently. If there are any concerns or unexpected issues it's important to get them checked out away.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Sterilization and Hygiene During Insertion
Following procedures reduces the chances of infections significantly.It is important to sterilize all equipment to usage and for providers to wear protective attire.
Patient Education on Device Care and Warning Signs
Educating patients about what to expect, including potential side effects and signs of complications, is crucial. Clear communication builds trust and promotes adherence to follow-up schedules.
Emergency Protocols for Complications
Providers should have protocols in place to address emergencies such as perforation, severe pain, or signs of systemic reactions. Immediate intervention can prevent long-term complications.
Mirena IUD FAQ
- What are the side effects of a Mirena?
- What is the advantage of Mirena?
- How long do Mirena IUDs last?
- What is the purpose of the Mirena IUD?
- What are the disadvantages of the Mirena IUD?
- What happens when Mirena is removed?
- Will Mirena cause weight gain?
- Who should not use Mirena?
- Can you get pregnant on Mirena?
- How to tell if Mirena is wearing off?
- What are the side effects of using Mirena?
- What happens if you leave a Mirena IUD in too long?
- Does Mirena start working immediately?
- Is Mirena bad for your liver?
- What is the biggest risk of IUD?
- Is Mirena insertion painful?
- Is Mirena safe?
- How do you know if you have an infection from Mirena?
- Can Mirena cause ovarian cysts?
- Does Mirena stop periods?
What are the side effects of a Mirena?
Feeling a headache dealing with acne, experiencing breast soreness, and facing bleeding might improve within three months of starting to use it; also, mood swings and cramping or pelvic pain could occur.
What is the advantage of Mirena?
The Mirena IUD was the intrauterine device on the market offering protection against pregnancy for a span of up to eight years.
How long do Mirena IUDs last?
8 years
What is the purpose of the Mirena IUD?
The Mirena intrauterine device, which releases levonorgestrel hormone, helps prevent pregnancy for a duration of up to 8 years and provides relief for periods for a maximum of 5 years in women opting for birth control methods.
What are the disadvantages of the Mirena IUD?
Some women who use devices (IUDs) may develop a pelvic infection known as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID is commonly transmitted through activity, and the risk of contracting PID increases if either you or your partner engage in activities with multiple partners. PID can lead to complications like infertility and ectopic pregnancy, or persistent pelvic discomfort.
What happens when Mirena is removed?
Following the removal of a Mirena device (commonly referred to as an IUD), individuals may encounter bleeding and discomfort as potential side effects post-procedure.Alongside symptoms some individuals may also undergo challenges commonly referred to as the "Mirena crash."The Mirena IUD operates by releasing levonorgestrel, a version of progesterone into the cavity.
Will Mirena cause weight gain?
Mirena, being an IUD, can lead to weight increase primarily because of the hormone progestin triggering water retention and bloating issues.
Who should not use Mirena?
Mirena should not be used by women who are known or suspected to be pregnant or cannot use it for coital contraception. It is also not recommended for those with a congenital or acquired anomaly that includes fibroids causing distortion of the cavity. Additionally avoided are women with known or suspected breast cancer or other types of progestin cancer either, in the past.
Can you get pregnant on Mirena?
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a method of birth control that is known for its effectiveness, in preventing pregnancy. In some cases where an IUD may have shifted position or exceeded its duration of effectiveness. there is a possibility of getting pregnant while using an IUD. If pregnancy occurs while the IUD is still in place, it can lead to risks for both the individual and the unborn baby.
How to tell if Mirena is wearing off?
If you've been using the Mirena implant for some time now and notice an alteration in your cycle or its associated symptoms, it could be an indication that the implant is not functioning as intended.
What are the side effects of using Mirena?
It's quite common to notice variations, in your cycle while using Mirena as your method! These changes could show up as light spotting between periods, cycles, longer cycles, unpredictable bleeding patterns, extended periods of no bleeding at all, heavier flow during periods, and experiencing menstrual cramps from time to time. Just a few things that might happen when you're on this medication!
What happens if you leave a Mirena IUD in too long?
If your intrauterine device (IUD) remains in your uterus after its expiration date the main concern is the risk of developing infections that can potentially lead to infertility. Additionally, using an IUD may not provide contraception as intended.
Does Mirena start working immediately?
The Mirena intrauterine device starts working if it's placed within seven days of your period starting. If you get the Mirena IUD inserted at a time, in your cycle other than the first seven days of your period, like condoms for extra protection for at least one week after insertion. There's a chance that the IUD could shift out of place from the uterus.
Is Mirena bad for your liver?
can worsen liver problems
What is the biggest risk of IUD?
Perforation can lead to the IUD passing through the wall, which is considered an uncommon and risky complication associated with IUD use.
Is Mirena insertion painful?
The IUD is placed by doctors through the cervix into the uterus. Patients might feel anything from discomfort, to intense cramps while its happening.
Is Mirena safe?
Many women can generally use devices (IUDs). Certain situations may increase the likelihood of experiencing side effects or complications. Such as having current sexually transmitted infections (STIs), pelvic infections, or possibly being pregnant.
How do you know if you have an infection from Mirena?
Infections are not common. They should be addressed promptly because they can escalate quickly in severity. If you experience any of these symptoms;. Pain in the abdomen appears to be getting worse. New onset of pain, during sexual intercourse.
Can Mirena cause ovarian cysts?
Some individuals using Mirena IUD may experience a chance of developing ovarian cysts. this cyst typically resolves by themselves within a month. Although IUD.s are generally considered a method there is still a small risk of mortality associated with them.
Does Mirena stop periods?
Once you've been using Mirena for some time, you may notice a decrease in the number of days with bleeding and spotting. Some women experience a cessation of periods. Once Mirena is taken out your menstrual cycles are expected to resume. In cases where heavy bleeding is an issue, the amount of blood lost per cycle tends to decrease gradually with prolonged use.