Nadifloxacin Cream
- Introduction
- History and development of Nadifloxacin Cream
- General properties and characteristics
- How It Works
- Composition
- Uses
- Off-label Use
- Dosage and Administration
- Storage
- Interaction
- Warning
- Contraindication
- Careful Administration
- Important Precautions
- Administration to the Elderly
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Administration to Children
- Overdosage
- Handling Precautions
- Side Effects
- Common Side Effects
- Overview
Introduction
Dermatological therapeutics have seen advancements, and one of the noteworthy ones is the Nadifloxacin Cream. Exploring its history and characteristics gives us an understanding of its importance in present-day medicine.
History and development of Nadifloxacin Cream
Nadifloxacin Cream, a regarded advancement in the field of pharmacology has an interesting backstory. The creation of this cream was driven by the need to combat bacterial strains that caused skin conditions. In the years of the 20th century, researchers recognized the necessity for more powerful topical treatments.
Through research and rigorous clinical trials, Nadifloxacin was identified as an effective solution leading to the development of this cream. Its progression has been marked by improvements based on real-world observations and feedback, from patients.
General properties and characteristics
To truly grasp the intricacies of Nadifloxacin Cream it's important to have an understanding of its overall characteristics;
- Antibacterial Range; One of its qualities is its ability to combat a wide range of bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative types.
- Resistance Development; An interesting aspect of Nadifloxacin is that it takes time for resistance to develop. This means that its effectiveness remains consistent with prolonged use.
- Skin Compatibility; The way it's uniquely formulated allows for minimal absorption into the bloodstream making it perfect, for topical applications.
How It Works
The effectiveness of Nadifloxacin Cream relies on its way of working against bacteria, which distinguishes it from many other similar products.
Mechanism of action against bacteria
Nadifloxacin works by blocking the activity of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV enzymes, which are crucial for the replication of DNA. As a result, this interference leads to the outcomes;
- Causes fragmentation of DNA.
- Stops the division of bacterial cells.
- Results in quick death of bacterial cells, effectively eliminating the underlying cause of various skin infections.
Comparative efficacy with other topical antibiotics
When compared to topical antibiotics, Nadifloxacin often stands out as the better choice. While many antibiotics struggle with growing resistance, Nadifloxacin offers advantages; it can penetrate deeper into the affected area, reducing the likelihood of bacterial mutation and delaying the onset of resistance. Additionally, clinical trials have shown results when using Nadifloxacin to treat acne vulgaris.
Composition
The effectiveness and safety of any product depend on its composition and Nadifloxacin Cream is no different.
Active and inactive ingredients
The main component that makes Nadifloxacin Cream effective is undoubtedly its ingredient called Nadifloxacin. However, the cream also contains inactive ingredients that are important, for maintaining its stability and ensuring patient comfort. Some of these ingredients can include
- Emollients, which help in the application;
- Preservatives, which extend the shelf life of the cream;
- Thickeners, which help in achieving the desired consistency.
Pharmaceutical form and characteristics
Nadifloxacin Cream is commonly available in a uniform, off-white texture. It comes in aluminum tubes designed to prevent contamination and make it easy to apply. The cream's consistency and pH level are carefully balanced to minimize skin irritation while providing therapeutic benefits.
Uses
The various uses of medications often demonstrate the creative thinking of the medical field. In terms of treatments, they cover a wide range of conditions, each highlighting the complex nature of the human skin system. One such adaptable solution focuses on the following;
Acne vulgaris treatment
Acne vulgaris, a known skin condition that can affect one's appearance, has found a powerful solution. The challenges of puberty or hormonal changes often lead to skin blemishes such as pimples, nodules, and cysts. The treatment in question; (1)
1. Eliminates Propionibacterium acnes, the main culprit behind the inflammation and resulting pus-filled pimples. (2)
2. Helps regulate sebum production, reducing the environment that promotes bacterial growth.
3. Exfoliates the skin, clearing clogged pores and creating a path for renewed and revitalized skin.
Acne Vulgaris
Bacterial skin infections
The skin is often vulnerable to types of harmful bacteria. From staphylococcal colonies to more dangerous strains like streptococcus the skin's natural defense can be easily overcome. Using this treatment offers benefits; (1)
1. It provides antimicrobial action, effectively eliminating a wide range of bacteria.
2. It helps speed up the healing process by enhancing the skin's regenerative abilities.
3. It also acts as a measure against future infections.
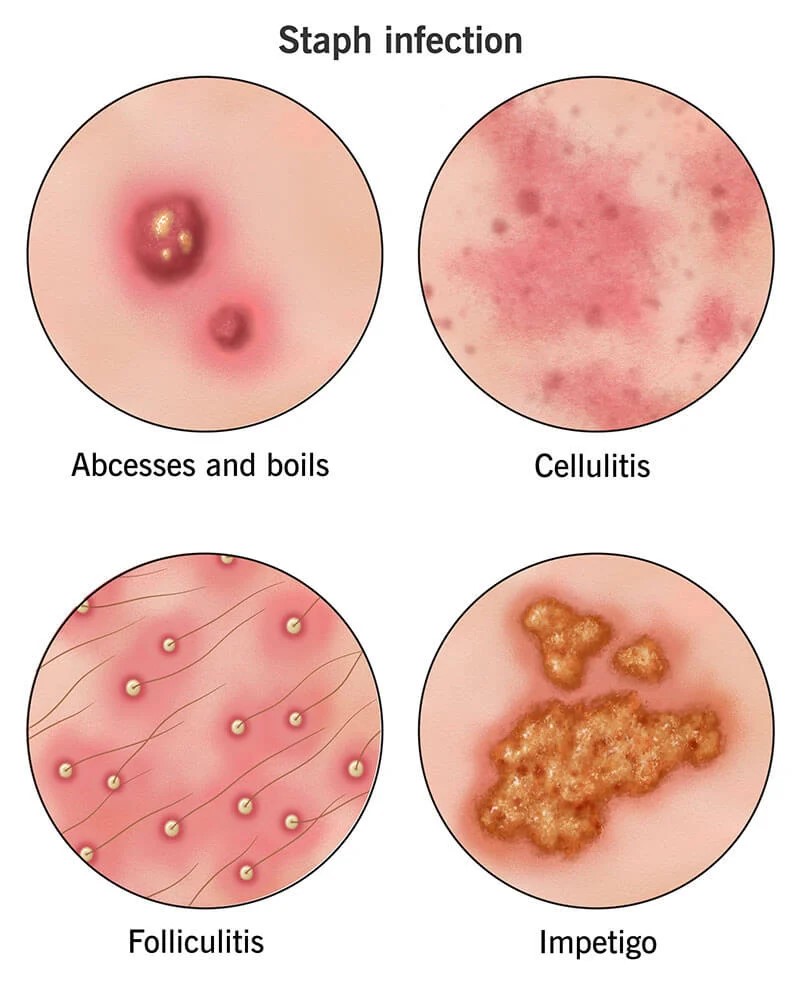
Staphylococcal Infection
1. Wikipedia - Nadifloxacin
Post-surgical infections
Surgeries, while necessary, can sometimes lead to complications. One of the concerns after surgery is the risk of infections. These infections are caused by microorganisms that can be found in hospitals and need to be treated.
The treatment we're discussing here helps prevent these microorganisms from colonizing incisions, making sure the surgical site stays clean and reducing the chances of severe infections. It works alongside antibiotics to fight against bacteria in a two-pronged approach.
Overall, this versatile treatment plays a role in maintaining skin health by protecting it from both common and uncommon bacterial threats.
Off-label Use
Throughout history, healthcare experts have frequently resorted to off-label utilization as a remedy for medical dilemmas. This unconventional approach amidst the complexities of boundaries presents a range of therapeutic options that initially seem unrelated to the drug's primary purpose.
Potential applications in dermatology
Dermatology, a field that is constantly exploring ideas and innovations, has discovered numerous potential uses for off-label treatments. Whether it's a skin issue or a stubborn dermatological problem these treatments offer hope. Some examples include;
1. Soothing Psoriasis; Certain medications originally designed for diseases have shown effectiveness in reducing psoriasis flare-ups.
2. Addressing Melasma; Drugs developed for disorders might surprisingly have the ability to lighten dark patches associated with melasma.
3. Treating Telangiectasias; Interestingly, certain blood pressure medications can be applied topically to constrict blood vessels and alleviate spider veins.
These findings demonstrate how dermatology is continuously uncovering possibilities, for the benefit of patients.
Studies and findings on off-label benefits
Although the use of medications for purposes other than their intended ones may seem accidental it is supported by extensive research and validation. Scholars and dermatologists have dedicated hours to exploring the fields of pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics to uncover these hidden benefits. Some notable discoveries include;
1. The Revolution of Retinoids; Initially recognized for their effectiveness in treating acne, further studies have revealed their ability to reduce wrinkles and mitigate the effects of photoaging.
2. Altruistic Antifungals; Upon examination, certain antifungal agents have exhibited commendable anti-inflammatory properties making them valuable in treating specific eczematous conditions.
3. Curious Corticosteroids: In addition to their known anti-inflammatory role, corticosteroids have shown potential in treating stubborn fungal infections when combined with traditional antifungal agents.
In essence, the exploration of off-label use showcases the determination of the medical community. It represents a pursuit of knowledge, a desire to heal, and an insatiable curiosity that drives medical progress as new therapeutic avenues are discovered.
Dosage and Administration
The effectiveness of a medication often depends not only on its inherent qualities but also on how precisely it is administered. It is crucial to ensure that the right amount of medication is paired with the method and duration to achieve successful therapeutic outcomes.
Recommended dosages for various conditions
When it comes to treating conditions, it is important to customize the dosage of medication accordingly;
- For Acne Vulgaris; Apply a thin layer once a day, preferably at night, to maximize absorption and minimize exposure to UV rays.
- For Bacterial Skin Infections, Apply an amount to the affected area twice a day to ensure sufficient antimicrobial coverage.
- For PostSurgical Prophylaxis; Apply an appropriate amount evenly depending on the size of the surgical area in order to prevent any opportunistic infections.
Application methods
The key to topical treatments goes beyond the product itself and extends to how it is applied;
- Start with a clean and dry skin surface for maximum absorption.
- Use a dab and spread method to ensure the product is evenly distributed on the desired area.
- Avoid rubbing and instead use gentle straight strokes for absorption.
Duration of treatment
It is important to follow the recommended time frame to prevent any resistance and ensure that the issue is fully resolved. In the case of conditions treatment usually lasts for 7 to 14 days depending on how well the patient is improving. However chronic ailments may require a period of treatment often lasting for several weeks to months with close supervision, from a dermatologist.
Storage
The quality and effectiveness of a product are closely tied to how it is stored. It is crucial to provide the conditions to preserve its therapeutic properties and ensure its safety.
Optimal storage conditions
Every product performs best under environmental conditions. It is recommended to keep the temperature between 20°C to 25°C, although slight variations are usually acceptable. To prevent degradation it is beneficial to maintain a humidity below 60%. Additionally, preserving the ingredients is aided by keeping the environment dim and free, from ultraviolet light.
Shelf life
Normally starting from when it's produced the product maintains its effectiveness for a period of 24 to 36 months as long as it remains unopened and stored in accordance, with the recommended instructions.
Precautions against contamination
To ensure that topical preparations remain free from contaminants, it is important to clean your hands thoroughly before applying them. After each use, make sure to close the product. Additionally avoid contact, between the nozzle or tube opening and your skin to prevent any potential contamination.
Interaction
Some medications may lose their effectiveness. Even become harmful if they are taken together with substances that don't go well with them.
Drugs and substances that may interact
Interactions can be complex, especially when using topical agents at the same time. For example, using retinoids alongside products may increase dryness or irritation. Additionally, combining antibiotics with these agents might affect their effectiveness. It's also important to be cautious with products that contain levels of alcohol as they can cause excessive drying or compromise the skin's protective barrier.
Potential impact on the cream's efficacy
Interactions between substances can lead to a range of results;
1. The effectiveness of the treatment may decrease because the substances work against each other.
2. Side effects can become more pronounced when negative reactions from substances combine or amplify each other.
3. The way the active ingredient is absorbed or works in the body can be changed due, to interactions potentially affecting its impact.
Recommendations to avoid interactions
To avoid any issues during interactions, it is important to inform your dermatologist about all the topical and systemic medications you are currently using. Make sure to give each product time to be absorbed before applying the next one. If you're unsure about how your skin will react, it's always an idea to do a patch test first. In conclusion, while the process of using medication may seem complex, by applying it, storing it properly, and being aware of possible interactions, you can fully benefit from its intended effects.
Warning
In the field of pharmaceuticals, the main focus is on providing relief through measures. However, it is equally important to be aware of any risks or dangers involved. These warnings act as guiding lights helping patients and healthcare providers navigate through the world of medication intricacies.
Situations where usage should be reconsidered
While a medication may seem like a cure-all for many, there are situations where it is important to pause and reflect.
- These include pregnancy and lactation, as the impact on the developing fetus or newborn baby is still uncertain due to absorption through the skin.
- In geriatric populations with different skin barrier functions and metabolic rates, there is a possibility of increased sensitivity.
- Additionally, if someone has skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis, applying this medication might worsen their symptoms, so it's worth reconsidering its use in such cases.
Known adverse reactions
The field of medicine, although mostly beneficial, can sometimes have effects.
- These effects include irritation, which can vary from mild redness to severe burning.
- Another occasional but significant outcome is hyperpigmentation, where the treated areas may appear darker in color.
- In some cases, systemic uptake of medication through the skin might lead to symptoms, like dizziness or gastrointestinal issues.
Contraindication
Though the field of medicine offers a range of treatment options it is important to know when a specific approach could potentially do more harm, than good.
Health conditions that prohibit use
Medical records often contain stories about the characteristics of individuals, which can sometimes require caution. If someone has liver dysfunction, their liver might have difficulty processing certain substances, leading to higher levels in the body. Any past experiences of reactions or hives to similar substances are strong reasons to be careful. If someone has a compromised skin barrier due to conditions like ichthyosis or xerosis, there is an increased risk of absorbing substances and experiencing side effects throughout the body.
Medications that conflict
Careful Administration
Monitoring and regular check-ups
Continuous monitoring remains essential for achieving the treatment results;
- Initial Evaluation; An initial assessment that includes evaluating the severity of the condition and any possible side effects.
- Regular Check-ins; Scheduled reviews every two to four weeks particularly, during the early stages of treatment allow for timely interventions.
- Final Consultation; After completing the treatment, a final evaluation is conducted to ensure resolution and address any remaining concerns.
Recognizing and addressing mild side effects
The subtle manifestations of side effects require an observation;
- Mild Redness; It usually goes away on its own and doesn't require any action. However if it persists adjusting the dosage may be necessary.
- Itchiness; Applying a compress or using over-the-counter calamine lotions often help relieve the discomfort.
- Peeling; This is a result of skin renewal and can be reduced by regularly applying moisturizers.
To conclude, the principle of medicine has always emphasized: "first, do no harm”. Meaning that avoiding harm should be a priority. With knowledge, attentiveness, and caution, both healthcare professionals and patients can confidently navigate their treatment journey with safety, in mind.
Important Precautions
In the field of pharmaceuticals, it is crucial to administer remedies with accuracy. The way these treatments are delivered can make a difference between achieving positive results and facing unintended consequences. Therefore providing instructions about these precautions is not just a recommendation but absolutely essential.
Avoiding sunlight and UV exposure
When it comes to medications that can be affected by sunlight or those that make the skin sensitive, it's important to be cautious. The combination of UV rays and these medications can have effects such as reducing the effectiveness of the medication and increasing sensitivity to light resulting in redness, blisters, or even skin conditions caused by exposure to light. Additionally, it can potentially disrupt our skin's natural defense mechanism by altering its microbiota.
Use in combination with other products
When using skincare products together, it's important to have a good understanding of each one to ensure they work well together instead of causing any problems. Here are some guidelines to follow;
1. Order of Application: Start with formulations before applying denser ones. This helps the skin absorb the products effectively.
2. Give It Some Time: Allow a gap between applying products to avoid any potential conflicts between their ingredients that might cancel out their effects.
3. Ingredient Compatibility; Be mindful of combining ingredients that could potentially deactivate or counteract each other's benefits.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your skincare routine achieves the desired results without any interactions between the products you use.
Administration to the Elderly
The elderly population, with their physiological characteristics, faces a range of unique challenges and factors to be considered when it comes to skin-related pharmacotherapy.
As time passes, our skin goes through changes that require customized treatment approaches. When the epidermis becomes thinner, it becomes more prone to absorbing substances through the skin. Reduced sebaceous activity can lead to dryness so it's important to use moisturizers at the time. When there is a decrease, in supply it may affect how well our bodies clear compounds that are absorbed into our system.
Dosage adjustments if necessary
Considering the age-related changes mentioned earlier, it would be wise to adopt approaches in pharmacological management. These strategies could include;
1. Decreased Dosage: To prevent absorption into the body.
2. Extended Time Intervals: Taking into account the metabolic processes.
3. Conducting Spot Tests and evaluating for any increased sensitivities or adverse reactions.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Providing relief to pregnant or breastfeeding women presents an additional level of complexity as we must carefully weigh the benefits for the mother while considering any potential risks for the unborn or newborn baby.
Known effects on fetal development
When medications pass through the barrier, they interact in a complex way with the environment surrounding the developing embryo. This interaction can have effects;
1. Teratogenicity; There is a possibility that medications may cause functional abnormalities.
2. Impaired Organogenesis; This is especially relevant during the trimester when important embryonic development takes place.
3. Delayed Intrauterine Growth; Changes in blood flow to the direct effects on the fetus can result in slower growth.
These factors highlight the relationship between medications and embryonic development within the womb.
Transfer through breast milk
Breastfeeding is a nourishing experience, but it's important to be aware that some medications can pass into breast milk. The size of the drug molecules plays a role, as smaller molecules are more likely to enter breast milk. Additionally, differences in pH levels can cause certain medications to become trapped in the milk.
These factors can have effects on the baby ranging from minor digestive issues to more serious neurological impacts. In summary, it's crucial to prioritize the principle of "do no harm" when considering medication during breastfeeding.
With knowledge and careful consideration, navigating pharmacotherapy, for infants, older individuals, or expectant mothers can be done responsibly and confidently.
Administration to Children
In the field of treatments, it's important to recognize that children are different, from adults. Their unique physiology requires attention especially when it comes to using medications.
Age-specific recommendations
During childhood which's a complex period of growth and development it is important to consider a gradual approach when it comes to medication. Here are some factors to keep in mind for age groups;
For neonates (newborns) their renal and hepatic functions are still developing, so dosages need to be adjusted accordingly.
- Infants have a higher percentage of body water, which can impact how drugs are distributed in their system.
- Children between the ages of 2 and 12 tend to have rapid metabolic rates, which may require more frequent dosing.
- Adolescents are approaching adulthood. Their physiology is changing, including unique hormonal changes that should be taken into account.
Understanding these distinctions helps ensure that medication is appropriately tailored to each stage of childhood.
Potential side effects in pediatric patients
Children receiving treatment may experience a wide range of side effects due to their developing bodies. These can include delays in their progress gastrointestinal issues such as feelings of nausea or discomfort in the abdominal area various neurological symptoms ranging from mild drowsiness to severe seizures and disruptions, in their endocrine system which could impact growth and the timing of puberty.
Overdosage
The saying "excessive indulgence, in something can have negative consequences " holds true when considering the issue of taking too much medication.
Recognizing symptoms of excessive use
The risk of overdosing becomes a concern when medication is taken casually. It's crucial to recognize the indicators;
1. Systemic Symptoms; These can include feeling lightheaded, experiencing heartbeats, or having trouble breathing.
2. Dermatological Manifestations: Look out for skin issues, like rashes, blisters, or heightened redness.
3. Neurological Changes; Pay attention to any shaking, confusion, or loss of consciousness.
4. Gastrointestinal Disturbances; If you're experiencing vomiting, diarrhea, or stomach cramps, it might be a sign of an overdose.
It's important to be mindful of these symptoms and seek attention if they occur.
First-aid and medical interventions
Quickly identifying an overdose should be accompanied by actions;
Discontinuation; Stop giving the medication as soon as possible.
Supportive Care; Make sure the person stays hydrated keeps their airways clear and monitor their signs.
Specific Antidotes; If they are accessible they can counteract the effects of the medication.
Medical Consultation; In cases seeking urgent medical attention at a hospital might be necessary.
Handling Precautions
The journey towards achieving therapy is filled with potential challenges if proper precautions are not taken seriously.
Avoiding contamination
It is absolutely essential to keep medications in their state. Here are some important guidelines to follow;
1. Sterile Technique; When dealing with medications that need reconstitution or injections, it is crucial to maintain an environment.
2. Avoid Touching; This is particularly important when handling dropper tips or ointment tubes to prevent any contamination.
3. Storage; Always store medications at the recommended temperatures and away, from any contaminants.
Remember, following these practices ensures the integrity and effectiveness of medications.
Safe disposal methods
Promoting eco disposal of expired or unused medications; How Medication Take Back, Programs Help Protect the Environment. Avoiding water contamination; Why Flushing Medications is Not Recommended. Safe disposal in trash, Ensuring the safety of children and pets when no other options are available.
Side Effects
Medications although intended to be beneficial come with the edged risk of potential side effects.
Overview of known side effects
Regardless of their abilities all medications have the potential to cause a wide range of unintended effects. These can vary from temporary symptoms, to more serious and long lasting complications.
Common Side Effects
Although the world of medicine offers a range of options there are certain common side effects that often accompany them.
Frequently reported reactions
In the field of pharmacovigilance, it is often observed that certain reactions commonly occur. These include effects such as itching, redness, or mild swelling at the site of application. Gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, slight stomach discomfort, or a decrease, in appetite, may also be experienced. Additionally, some systemic reactions could occur, such as dizziness, headaches, or temporary fatigue.
Management and mitigation
When faced with these side effects, there are steps that can be taken to lessen their impact;
1. Adjusting the dosage; Gradually increasing or decreasing the amount or frequency of the medication.
2. Using medications; Giving antihistamines to address any reactions, for example.
3. Trying formulations; Switching to a different form or compound of the medication that has similar therapeutic benefits.
These proactive measures can help minimize the impact of side effects.
Overview
Medications, which form the foundation of medical treatments, require careful attention when being administered. Whether we are dealing with children managing the risk of overdosing or addressing side effects, it is crucial to approach medication administration with knowledge and caution. In this interaction, between illness and treatment, the guidance of healthcare experts serves as a steadfast guide to ensure patient safety, effectiveness of treatment, and overall well-being.