Phenoxybenzamine Injection
- I. Introduction to Phenoxybenzamine Injection
- II. Uses of Phenoxybenzamine Injection
- III. Off-Label Uses of Phenoxybenzamine Injection
- IV. How Phenoxybenzamine Injection Works
- V. Dosage and Administration of Phenoxybenzamine Injection
- VI. Composition of Phenoxybenzamine Injection
- VII. Storage Requirements for Phenoxybenzamine Injection
- VIII. Interactions with Other Medications
- IX. Warnings and Precautions
- X. Contraindications for Phenoxybenzamine Injection
- XI. Careful Administration Considerations
- XII. Important Precautions
- XIII. Administration to Elderly Patients
- XIV. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- XV. Administration to Children
- XVI. Overdosage and Management
- XVII. Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
I. Introduction to Phenoxybenzamine Injection
Overview of Phenoxybenzamine
Phenoxybenzamine is an alpha-adrenergic blocker commonly used in healthcare for its ability to constrict blood vessels. It works by binding to alpha receptors, reducing the impact of natural vasoconstrictors in the body.
Purpose of Phenoxybenzamine Injection in Medical Practice
Phenoxybenzamine injections are mainly used in individuals with pheochromocytoma for surgery by easing symptoms and stabilizing blood pressure. They are also given to address the long term effects of this condition.
II. Uses of Phenoxybenzamine Injection
Treatment of Pheochromocytoma
Management of Hypertension in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
Use in Vasospasm Conditions
III. Off-Label Uses of Phenoxybenzamine Injection
Investigational Uses in Cardiovascular Disorders
Potential Applications in Raynaud's Phenomenon
Phenoxybenzamine is currently under investigation, for its ability to help alleviate the spasms linked to Raynauds disease by widening blood vessels thus improving circulation to the extremities and reducing the chances of tissue harm.
Other Experimental Uses in Endocrine Disorders
Disorders related to the imbalance of catecholamines in the endocrine system could find relief through the stabilizing properties of Phenoxybenzamine presenting treatment options, for these complex conditions.
IV. How Phenoxybenzamine Injection Works
Mechanism of Action: Alpha-Adrenergic Blockade
The medication permanently attaches to alpha 1 and alpha two adrenoceptors, blocking the vasoconstriction caused by agonists and leading to vasodilation.
Effects on Vasodilation and Blood Pressure Regulation
Phenoxybenzamine helps control blood pressure in patients, with catecholamine release, by reducing peripheral resistance and arterial pressure.
V. Dosage and Administration of Phenoxybenzamine Injection
Recommended Dosage for Pheochromocytoma
In the beginning, the dosage is usually started at a level and then slowly increased to reduce any potential risks. The ongoing doses are modified based on how the reacts and their ability to tolerate the medication.
Administration Routes: Intramuscular vs. Intravenous
When giving medication through a vein the effects are quick. Administering it into the muscle ensures a gradual release, which is better, for long term treatment.
Adjustment of Dosage Based on Patient Response
It is essential for healthcare professionals to closely monitor patients responses to treatment and any potential side effects in order to make adjustments, to the dosage.
VI. Composition of Phenoxybenzamine Injection
Active Ingredients and Chemical Structure
Phenoxybenzamine hydrochloride, the component, is a type of haloalkyl amine that acts by obstructing alpha-adrenergic receptors.
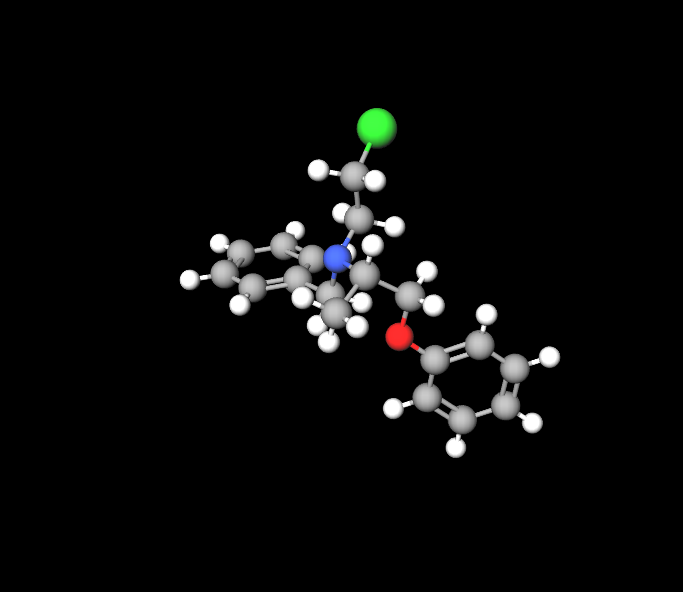
Pharmaceutical Formulation Details
The Phenoxybenzamine injection is carefully crafted to maintain stability and improve absorption in the body with added solvents and stabilizers to boost its effectiveness and prolong its shelf life.
VII. Storage Requirements for Phenoxybenzamine Injection
Temperature and Environmental Conditions
Phenoxybenzamine injection should be kept in a controlled environment to ensure its effectiveness. Its best stored at temperatures ranging from 2°C to 8°C (35.6°F, to 46.4°F). Make sure to shield it from sunlight and high temperatures as these conditions may compromise the potency of the injection.
Shelf Life and Stability
The effectiveness of Phenoxybenzamine is greatly influenced by following the storage guidelines. Generally the injection remains effective, for around 24 months under storage conditions. Beyond this timeframe there is a possibility that the medication may lose its effectiveness underscoring the significance of checking expiration dates.
VIII. Interactions with Other Medications
Potential Drug Interactions with Hypertension Medications
Phenoxybenzamine may have weaker effects when combined with other medications for high blood pressure. For example, taking it together with beta-blockers can boost its effectiveness in lowering blood pressure. It could also lead to a significant drop in heart rate. These interactions require monitoring, during treatment.
Interaction with Anesthesia and Anesthetic Agents
Phenoxybenzamines ' blocking abilities can impact the outcomes of drugs, especially those affecting sympathetic nervous system activity. Anesthesiologists need to adjust doses to prevent low blood pressure risks during surgeries.
IX. Warnings and Precautions
Cardiovascular Risks and Monitoring
- Patients receiving Phenoxybenzamine treatment individuals with existing heart issues should be closely watched for possible heart related side effects such, as low blood pressure and reflexive rapid heartbeat.
- It is advised to conduct heart evaluations to address these concerns proactively.
Allergic Reactions and Hypersensitivity
Although uncommon allergic responses can happen with Phenoxybenzamine. Signs could vary from skin irritations to serious anaphylactic reactions. Seeking medical help is vital, at the initial indication of hypersensitivity.
Precautions in Patients with Renal Impairment
Patients, with kidney problems should be careful when using phenoxybenzamine. Because their bodies may not clear the medication effectively they have a higher chance of experiencing negative effects. It's important to adjust the dosage according to their kidney function test results.
X. Contraindications for Phenoxybenzamine Injection
Absolute Contraindications Based on Medical Conditions
Phenoxybenzamine should not be used in patients with conditions such as heart attacks, severe low blood pressure, and fluid accumulation in the lungs, as blocking alpha receptors could worsen the patient's condition.
Use in Patients with Known Allergies or Sensitivities
People who have hypersensitivity to Phenoxybenzamine or any of its ingredients should avoid taking this medication as it may cause serious allergic reactions.
XI. Careful Administration Considerations
Monitoring Blood Pressure During Administration
It's crucial to keep an eye, on blood pressure when giving Phenoxybenzamine especially at the start of treatment to handle orthostatic hypotension effectively.
Titration of Dosage in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals frequently need adjustments in medication doses because they are more prone to experiencing negative effects and have multiple health conditions. Incrementally adjusting the dosage of Phenoxybenzamine can reduce risks and lead to the desired treatment results.
Phenoxybenzamine for cats
Phenoxybenzamine is administered to dogs and cats experiencing challenges in urination caused by muscle spasms in the urinary tract. This medication helps alleviate the spasms making it easier and more comfortable for them to pass urine. Additionally, it is prescribed to manage the symptoms of an adrenal gland tumor known as phaeochromocytoma.
XII. Important Precautions
Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Pregnant women and nursing mothers should only take Phenoxybenzamine if the advantages outweigh the risks to the baby. It's essential to think about this medication since it can pass through the placenta and into breast milk.
Pediatric Administration Considerations and Dosage Adjustments
Extreme care is taken when administering phenoxybenzamine to children. Adjustments, in dosage are required depending on the childs weight and the particular medical condition being addressed, with close monitoring to prevent any outcomes.
XIII. Administration to Elderly Patients
Age-Related Considerations in Dosage and Monitoring
Elderly individuals may show increased sensitivity to Phenoxybenzamine, which could necessitate dosage modifications and closer monitoring for orthostatic reactions. This age group commonly has health conditions that might affect how the drug works in their bodies.
XIV. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Risks and Benefits Assessment
Before using Phenoxybenzamine during pregnancy and breastfeeding it is important to evaluate the risks and benefits. The choice to give the medication should depend on whether the expected advantages for the mother are greater than any potential harm to the unborn child or breastfeeding baby.
Potential Effects on Fetal Development and Breastfeeding
Research conducted on animals has indicated risks to the growth of fetuses when Phenoxybenzamine is used, but there is a lack of well-regulated studies on humans. The need for caution and thorough discussion with the patient arises due to the drug's likelihood of being excreted in milk.
XV. Administration to Children
Pediatric Dosage Guidelines
Calculating the right medication doses for children requires measurements that consider body size or weight. The goal is to reduce reactions and ensure the desired medical outcome.

Safety and Efficacy Considerations in Pediatric Patients
The safety and effectiveness of Phenoxybenzamine in children have not been completely confirmed. There is data, from clinical trials and studies highlighting the importance of using it carefully and monitoring closely.
XVI. Overdosage and Management
Symptoms of Overdose
Signs of an overdose may involve low blood pressure, breathing difficulties, and feeling drowsy. It is crucial to seek medical help to address these serious situations.
Treatment Protocols and Supportive Care
When dealing with an overdose of Phenoxybenzamine the main approach involves providing supportive treatment. This includes ensuring airway, breathing, and circulation while considering the use of vasopressors if needed.
XVII. Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Safe Handling Practices During Preparation and Administration
Healthcare workers need to follow safety protocols when dealing with Phenoxybenzamine to avoid exposure. This involves wearing gear and avoiding direct contact, with the skin or eyes.
Disposal of Unused Medication and Sharps
It is important to follow disposal procedures to reduce harm to the environment and avoid misuse. Any unused medications and sharp objects should be thrown away following the guidelines set by regulations and safety protocols, for dangerous waste materials.











