Silymarin
- I. Introduction to Silymarin
- Approved Uses of Silymarin
- Off-Label Uses of Silymarin
- IV. Silymarin Dosage and Administration
- V. Side Effects of Silymarin
- VI. Drug Interactions with Silymarin
- VII. Contraindications for Silymarin Use
- VIII. Careful Administration of Silymarin
- IX. Specific Populations
- X. Overdose of Silymarin
- XI. Storage of Silymarin
- XII. Handling Precautions
- XIII. Warnings for Silymarin Use
- XIV. Conclusion: Summary of Silymarin's Benefits and Risks
I. Introduction to Silymarin
A. Brief Overview and History
Silymarin, a compound extracted from the milk thistle plant (Silybum marianum), has a history that can be traced back to ancient times. This plant was highly regarded in civilizations like Ancient Greece and Rome, where it was utilized for its believed healing abilities. Recently, scientists have extensively studied silymarin for its potential to protect the liver and act as an antioxidant. These studies have revealed its prospects in the hepatology field, particularly in treating various liver diseases.
B. Chemical Structure and Composition
The potent properties of Silymarin are rooted in its chemical structure. Silymarin, a flavonoid, consists of three main compounds; silybin (also known as silibinin) silydianin, and silychristin. Among these, silybin is the most active, making up approximately 50-70 % of the Silymarin complex. Silybin is a combination of two diastereoisomers, silybin A and silybin B, present in equal amounts. While silydianin and silychristin are not as abundant as silybin, they still play a role as components accounting for approximately 20-30 % of the Silymarin extract. The unique blend of these compounds contributes to Silymarin's pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential.
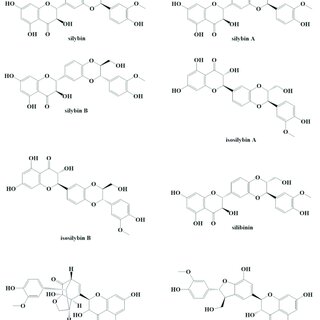
C. How Silymarin Works: Pharmacological Action
The effectiveness of Silymarin can be attributed to its pharmacological actions. Primarily it demonstrates antioxidant properties by scavenging free radicals and increasing glutathione levels, an essential antioxidant in the body. Additionally, Silymarin possesses inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. It works by inhibiting the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF kB), a key mediator of inflammatory responses. By blocking the NF kB pathway, Silymarin reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines, thereby controlling inflammation. In terms of liver protection Silymarin improves liver function by stabilizing hepatocyte membranes and reducing damage to cells and fibrosis. Moreover, it has therapeutic applications in managing various cancers and can influence apoptosis pathways. Combining these actions makes Silymarin highly valuable in natural and pharmacological compounds.
Approved Uses of Silymarin
Use in Liver Diseases
Silymarin, a flavonoid derived from the milk thistle plant’s seeds, has been a remedy for liver issues for centuries. Here are some of the approved applications of silymarin in liver diseases:
- Alcoholic Liver Disease: Silymarin has proven effective in treating alcoholic liver disease by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver, thereby preventing damage.
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Silymarin has also shown effectiveness in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, protecting against further harm.
- Hepatitis: Silymarin is known to be an effective treatment for hepatitis by decreasing inflammation and oxidative stress, thus preventing additional damage1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Silymarin:
Use in Diabetes Management
Silymarin is a flavonoid extracted from the seeds of the milk thistle plant. It has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies have shown that silymarin can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels in people with diabetes1.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
- Insulin Sensitivity Factor: What You Should Know - Healthline
- Insulin sensitivity factor: What is it and how to test for it? - Medical News Today
- Milk thistle - Mayo Clinic
Other Official Uses
Silymarin is a flavonoid extracted from the seeds of the milk thistle plant. It has been used for over 2,000 years as an herbal remedy for various ailments, particularly liver, kidney, and gallbladder problems. Silymarin has also been utilized in official capacities, including the treatment of issues related to the gallbladder1, addressing cases of mushroom poisoning1, combating prostate cancer, and managing breast cancer1.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
- Milk thistle Information - Mount Sinai
- Anti-cancer Effects of Silibinin: The Current Status in Cancer … - SpringerLink
- Silymarin: A Potent Antioxidant, Liver Protector, and Anti-Cancer Agent - Smart Publications
Off-Label Uses of Silymarin
Anticancer Properties
Silymarin is a flavonoid extracted from the seeds of the milk thistle plant. It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and has been shown to possess various pharmacological properties like hepatoprotective, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and cardioprotective activities1. Silymarin has demonstrated its ability to impede the growth of cancer cells both in laboratory studies (in vitro) and in living organisms (in vivo)1. Additionally, silymarin possesses inflammatory properties that could lower the risk of cancer1.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
- Silymarin - 1mg
- Role of Silymarin in Cancer Treatment: Facts, Hypotheses, and Questions - Sage Journals
- Multitargeted therapy of cancer by silymarin - Europe PMC
Skin Health and Anti-Aging
Silymarin is a flavonoid extracted from the seeds of the milk thistle plant. It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and has been shown to possess various pharmacological properties like hepatoprotective, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and cardioprotective activities1. Silymarin has been discovered to possess properties that counteract the effects of aging. Studies have indicated its ability to diminish the visibility of lines and wrinkles on the skin23. Additionally, silymarin possesses antioxidant properties that can potentially safeguard the skin against damage caused by radicals3.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
- Silymarin - The Dermatology Review
- Polyherbal formulation with anti-elastase and anti-oxidant properties … - BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies
- Silymarin - The Ancient Hidden Antioxidant – Sachi Skin
Other Potential Off-Label Uses
Silymarin has been investigated for its potential in treating other health issues, including diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, depression, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, and viral hepatitis. However, further research is necessary to ascertain the efficacy of silymarin for these specific conditions.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
IV. Silymarin Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosage
Usually, Silymarin is taken orally with the recommended dosage of 140mg thrice daily. It's commonly suggested to take it with meals. It's important to note that this dosage is an estimate and might vary depending on individual needs and medical guidance.
B. Dosage Variations by Condition
The recommended amount of Silymarin may differ depending on the condition it is being used to treat. For example, when dealing with Alcoholic Liver Disease, taking a dosage of around 420 mg daily is often suggested. In the case of Type II Diabetes, a dose of 200 mg taken two or three times a day might be advised alongside conventional antidiabetic medication. These dosage adjustments are typically made based on factors such as the severity of the condition, how the patient responds to treatment, and the desired therapeutic outcome.
C. Administration Guidelines
Silymarin is usually taken by mouth as capsules, tablets, or as part of a combination supplement. It's advisable to consume it with enough water and take it alongside food to improve absorption. The duration of treatment can vary, lasting from a week up to several months, depending on the desired therapeutic outcome and how the patient responds.
V. Side Effects of Silymarin
A. Common Side Effects
Although Silymarin is typically well tolerated, it may lead to some temporary side effects. The frequently observed ones involve gastrointestinal issues, like bloating, diarrhea, and indigestion.
B. Less Common and Severe Side Effects
Occasionally a few patients may encounter pronounced adverse effects. These could include responses like a rash, itchiness, or hives. In some some instances, there have been reports of feeling nauseous and experiencing headaches and joint pain.
C. Long-Term Side Effects
The complete effects that may arise from using Silymarin over some time are still not completely understood due to the absence of studies conducted over an extended duration. Nevertheless, it is generally recommended that individuals who take any medication for a prolonged period should regularly consult with a healthcare professional to assess its continued usage.
VI. Drug Interactions with Silymarin
A. Interactions with Prescription Drugs
It is possible that Silymarin could have interactions with prescription medications. This is because Silymarin might influence the speed at which the liver metabolizes drugs. Some examples of these medications are statins, allergy medications, and specific antipsychotics. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting Silymarin, especially if you are already taking medications.
B. Interactions with Over-the-Counter Drugs
Similar to prescription medications over counter drugs can also interact with Silymarin, mainly if they go through liver metabolism. This includes pain relievers and cold medicines. Therefore, consult a pharmacist or healthcare provider if you're uncertain.
C. Interactions with Herbal Supplements
Silymarin could potentially interact with herbal or dietary supplements. It's worth noting that accessories like cohosh or kava which have an impact on the liver, might have their effects enhanced when taken together with Silymarin. As a result, it's advisable to exercise caution when using these supplements concurrently.
VII. Contraindications for Silymarin Use
A. Known Allergies
Individuals who have a known allergy to milk thistle or any other plants belonging to the Asteraceae/Compositae family, like daisies, marigolds, or chrysanthemums, are recommended to refrain from using Silymarin. If any signs of hypersensitivity reactions occur, such as skin rashes, itching, or difficulty, breathing it is essential to seek medical help.
B. Pre-existing Conditions
While Silymarin is generally considered safe, individuals with pre-existing conditions need to be cautious. Especially those with hormone conditions like breast, uterine, or ovarian cancer, endometriosis, or uterine fibroids should exercise caution since Silymarin might have estrogen-like effects, in the body.
C. Other Potential Contraindications
Patients who have surgical procedures should stop taking Silymarin at least two weeks before the system. This precaution is necessary to avoid bleeding as Silymarin can potentially delay blood clotting. Likewise, individuals with existing bleeding disorders should exercise caution when using Silymarin as it may elevate their risk of bleeding.
VIII. Careful Administration of Silymarin
A. Monitoring During Treatment
It is essential to monitor the progress of Silymarin treatment and monitor any potential side effects. It is essential to observe liver function tests for individuals who already have liver-related conditions. If any unexpected side effects occur, it is crucial to inform a healthcare professional.
B. Adjustments for Liver and Kidney Impairment
Patients with liver or kidney issues may require careful adjustment of Silymarin dosage to avoid excessive build-up in the body. Therefore it is crucial for healthcare providers to monitor the introduction of Silymarin in patients closely.
IX. Specific Populations
A. Administration to Elderly
Silymarin is usually regarded as an option for the elderly population. However, because older individuals often take medications and may have existing health conditions, it's important to start with caution and keep a watchful eye on their progress.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Although research on the use of Silymarin in women or nursing mothers is limited, it is generally recommended to be cautious due to the lack of available data. Therefore it is advisable to consult and seek approval from a healthcare provider before considering using Silymarin.
C. Administration to Children
The safety and effectiveness of Silymarin in children have not been thoroughly researched. Therefore, parents should consult a pediatrician who can assess Silymarin's suitability and appropriate dosage based on the child's age, weight, and overall health condition.
X. Overdose of Silymarin
A. Symptoms of Overdose
Although it is uncommon for someone to experience an overdose of Silymarin because the body can tolerate it well, consuming much could potentially result in specific adverse effects. These effects might include feelings of nausea, vomiting, stomach discomfort, and diarrhea. Furthermore, excessive intake could lead to a sense of weakness and a decrease in appetite, and in severe situations, it might even trigger an allergic response.
B. Management and Treatment of Overdose
If someone takes much Silymarin, the primary approach to managing it is by providing symptomatic and supportive care. It's essential to seek medical help if an overdose is suspected. The healthcare professional might observe the patient's signs, administer intravenous fluids if necessary and address any urgent symptoms. Additionally, they may need to reconsider or stop the dosage altogether based on how severe the overdose's.
XI. Storage of Silymarin
A. Recommended Storage Conditions
To ensure the quality of silymarin, it is best to store it in a dry location away from direct sunlight. The ideal storage temperature should generally be below 25°C (77°F). Moreover, it is essential to keep it out of the reach of children and pets to prevent consumption.
B. Proper Disposal of Unused Medication
It would be best if you did not throw away any leftovers. Expired Silymarin in your regular trash or flush it down the sink. Instead, returning it to a pharmacy or participating in a take-back program is better. This way, you can ensure that it is disposed of properly, which helps protect the environment and prevents any exposure or misuse.
XII. Handling Precautions
A. Safety in Handling
When working with Silymarin it's essential to be cautious and prevent any contact, with your eyes or open skin. In case of contact make sure to rinse with water. Always handle it in ventilated spaces and avoid directly inhaling the product.
B. Precautions in Case of Accidental Exposure
If someone accidentally ingests or comes into contact with this substance, it is essential to seek assistance immediately. Make sure to give the healthcare provider all the details about the type and amount of exposure and any symptoms that may have occurred afterward. It's also crucial to bring along the product's packaging or label when you go to a healthcare facility.
XIII. Warnings for Silymarin Use
A. General Warnings
Although Silymarin is generally well tolerated, it's essential to remember that specific individuals may experience reactions. For example, people who are sensitive to plants in the Asteraceae/Compositae family might have a response to Silymarin. Furthermore, individuals with hormone conditions should be cautious because Silymarin may have estrogen-like effects. Additionally, those with clotting disorders or those about to undergo surgery should also be aware of the blood thinning properties of Silymarin and take necessary precautions.
B. Drug Misuse and Dependence Potential
Thankfully Silymarin carries a risk of misuse or dependency since it doesn't produce any mind-altering effects or withdrawal symptoms. Nonetheless, it's crucial to remember that using it without medical guidance or for an extended period may result in undesired side effects or conceal the true origin of liver-related symptoms.
C. Use in Special Situations (e.g., Operating Machinery)
Based on what we know scientifically, Silymarin does not seem to affect alertness or coordination. Therefore it usually doesn't present a risk when using machinery or driving. However, suppose someone experiences dizziness, confusion, or other side effects that could impact their ability to move or make decisions. In that case, they need to avoid engaging in activities and seek advice from a healthcare professional.
XIV. Conclusion: Summary of Silymarin's Benefits and Risks
A. Weighing Pros and Cons
Silymarin has a range of benefits that make it appealing, such as safeguarding the liver providing antioxidant effects, and reducing inflammation. Many people with liver diseases, those related to alcohol or toxins, find it to be a popular choice. However, it's essential to be aware of risks like allergic reactions and interactions with other medications. Individuals with existing conditions, like hormone-sensitive issues or clotting disorders, should approach its use carefully.
B. Future Directions in Silymarin Research
Silymarin, with its range of potential health benefits, remains an area of great interest for researchers. Future studies have the potential to reveal applications for this powerful herbal supplement, enhance our understanding of how it works and refine the recommended usage guidelines. As we continue to learn more, it is highly likely that Silymarin will play a significant role in healthcare, offering patients additional safe and effective treatment options.
Silymarin FAQ
- Silymarin CF
- Silymarin benefits
- Silymarin milk thistle
- Silymarin in milk thistle
- Silymarin side effects
- Silymarin CF Skinceuticals
- Silymarin Skinceuticals
- Silymarin supplement
- Silymarin capsule
- Silymarin uses
- Silymarin complex
- Silymarin for dogs
- Silymarin dogs
- Silymarin vs milk thistle
- Silymarin for liver
- Silymarin liver
- Silymarin for skin
- Silymarin now
- Silymarin forte
- Silymarin dosage
- Silymarin dose
- Silymarin tablet
- Silymarin serum
- Silymarin pure encapsulations
- Silymarin phosphatidylcholine complex
- Silymarin advanced
- Silymarin extract
- Silymarin CF dupe
- Silymarin CF reviews
- Silymarin vitamin C
- Silymarin cream
- Is silymarin the same as milk thistle
- Silymarin milk thistle benefits
- Silymarin pronunciation
- Silymarin skincare
- Silymarin Amazon
- Silymarin Metagenics
- Silymarin plus
- Silymarin marianum
- Silymarin for fatty liver
- Silymarin fatty liver
- Silymarin Walmart
- Silymarin and breastfeeding
- Silymarin tea
- Silymarin CF vs Phloretin CF
- Silymarin skin
- Silymarin Walgreens
- Silymarin topical
- Silymarin Now Foods
- Silymarin phytosome
- Silymarin Genestra
- Silymarin milk thistle extract
- Silymarin or milk thistle
- How to use Silymarin CF
- Silymarin flavonoids
- Silymarin health benefits
- Is silybin the same as milk thistle
- Silymarin with Biosorb
- Silymarin for acne
- Silymarin for weight loss
- Silymarin vs silybin
- Is silymarin milk thistle
- Silymarin Reddit
- Silymarin structure
- Silymarin weight loss
- Silymarin dosage for dogs
- Silymarin plant
- Silymarin powder
- Silymarin acne
- Silymarin complex para que sirve
- Silymarin mechanism of action
- Silymarin complex side effects
- Silymarin complex benefits
- Silymarin CVS
- Silymarin breastfeeding
- Silymarin benefits liver
- Silymarin benefits for skin
- Silymarin foods
- Silymarin vs CE Ferulic
- Silymarin CF serum
- Silymarin milk thistle extract 300 mg
- What is silymarin for skin
- Silymarin complex California gold nutrition
- Silymarin USP
- Silymarin supplement benefits
- Silymarin melasma
- Silymarin capsule for fatty liver
- What does silymarin do for the liver
- Does silymarin cause liver damage
- Does silymarin really work
- Silymarin when to take
- When to take silymarin capsule
- What silymarin is good for
- Silymarin where to buy
- How to extract silymarin from milk thistle
- Liver aid silymarin capsule review
- What does silymarin do for the body
- Buy silymarin
- How much silymarin in milk thistle
- How much silymarin in milk thistle seeds