Sumatriptan
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Sumatriptan
- III. Off-Label Uses of Sumatriptan
- IV. How Sumatriptan Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition of Sumatriptan
- VII. Common Side Effects of Sumatriptan
- VIII. Serious Side Effects
- IX. Interactions with Sumatriptan
- X. Warnings and Precautions
- XI. Contraindications
- XII. Careful Administration of Sumatriptan
- XIII. Important Precautions with Sumatriptan
- XIV. Administration to Specific Populations
- XV. Overdosage of Sumatriptan
- XVI. Storage Conditions for Sumatriptan
- XVII. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
Sumatriptan, a prescription medication commonly used to address migraines and cluster headaches, is a serotonin receptor agonist. It works by impacting substances in the brain and narrowing blood vessels around the brain, providing relief from the throbbing or pulsating pain associated with these types of headaches. The development of Sumatriptan took place in the 1980s marking a significant advancement in our understanding and management of severe headaches such as migraines and cluster headaches. Following evaluation, Sumatriptan gained FDA approval in 1991. While initially approved for treating migraines, its indications were expanded to include cluster headaches.
II. Uses of Sumatriptan
Sumatriptan is commonly used to treat migraines and cluster headaches, effectively reducing the intense pulsating pain experienced during migraines. It is also recommended to alleviate the sharp, piercing pain accompanying cluster headaches. Sumatriptan works in treating headaches by stimulating serotonin (5 HT1) receptors in the brain123. This stimulation causes the muscles surrounding the blood vessels in the brain to contract, resulting in a narrowing of these vessels124. Consequently, this helps relieve headache pain by reducing blood flow24 and blocking the release of certain natural substances that cause pain, nausea, and other symptoms of migraine2.
1: Sumatriptan - Wikipedia 2: Sumatriptan: MedlinePlus Drug Information 3: Sumatriptan and Naproxen: Dosage, Mechanism/Onset of Action, Half-Life … 4: Sumatriptan: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action - DrugBank Online
III. Off-Label Uses of Sumatriptan
Chronic daily headaches are sometimes treated with Sumatriptan by healthcare professionals because it has the ability to constrict blood vessels in the brain123. While not its primary use Sumatriptan has also been prescribed for tension-type headaches45. Additionally, in cases of post-traumatic headaches caused by injury, Sumatriptan has been utilized due to its vasoconstrictive properties12.
1: Sumatriptan Injection: MedlinePlus Drug Information 2: Sumatriptan: MedlinePlus Drug Information 3: Sumatriptan: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action - DrugBank Online 4: Outpatient Primary Care Management of Headaches: Guidelines from … - AAFP 5: Sumatriptan: Side Effects, Dosage, Uses, and More - Healthline
IV. How Sumatriptan Works
Pharmacology; How it Works Sumatriptan acts on the 5 HT1 receptors in the brain's blood vessels, causing them to narrow. This narrowing is believed to be why migraine and cluster headaches are relieved. Pharmacokinetics; How it's Processed When taken orally, sumatriptan is quick. Its highest concentration in the bloodstream is usually reached within 2 hours. It spreads throughout the body, most broken down by an enzyme called monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) in the liver. The inactive byproducts are then mainly eliminated through urine.
V. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosages; The starting dose of Sumatriptan for adults is 25 mg, which can be adjusted to a maximum of 100 mg depending on how the patient responds and tolerates the medication. Forms and Strengths; Sumatriptan is available in various forms, such as tablets (25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg), nasal spray, and subcutaneous injections. Administration Methods; Depending on the severity and onset of the headache, Sumatriptan can be taken orally through the nose or injected under the skin. This provides flexibility in choosing a suitable method. Dosage Adjustment for Specific Populations; In patients with liver impairment, reducing the dose of Sumatriptan is recommended due to increased exposure to the medication in this population.
VI. Composition of Sumatriptan
The main component in Sumatriptan is called sumatriptan succinate, which acts on the serotonin receptor. Other ingredients not directly involved in the medication's effectiveness may include lactose monohydrate, cellulose, and triacetin. Sumatriptan comes in forms such as tablets, nasal sprays, and injections, giving healthcare professionals the flexibility to choose the most suitable administration method depending on each patient's requirements.
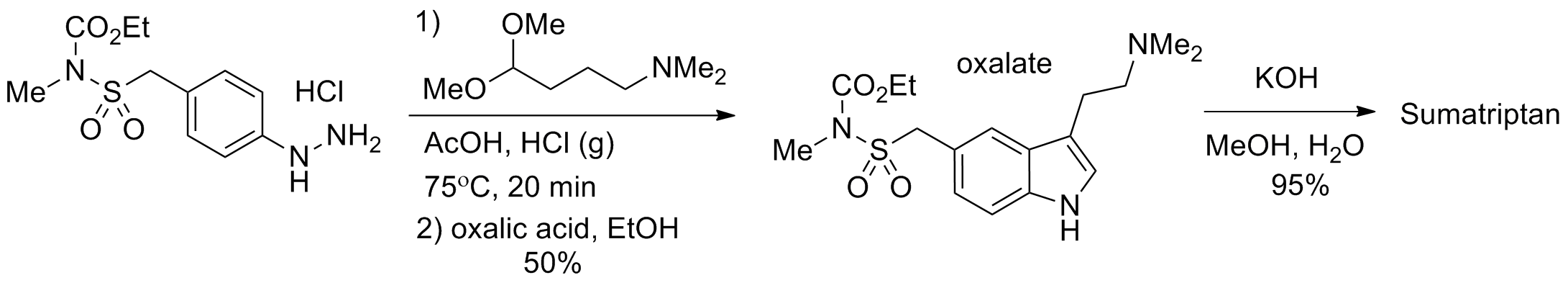
VII. Common Side Effects of Sumatriptan
Some mild side effects may include experiencing cold or numb sensations in various body parts. You might also feel a sense of heaviness or pressure in your chest, neck, or jaw. Additionally, you could experience drowsiness or fatigue. These side effects are usually temporary. Occur shortly after taking the medication. They typically go away on their own without needing any treatment.
VIII. Serious Side Effects
Warning Signs and Symptoms Rarely but in some cases, individuals may experience side effects such as chest pain, an irregular heartbeat, or intense abdominal pain. These symptoms are signs of a significant issue and should be taken seriously. It is crucial to seek medical attention if these severe side effects occur. Doing so will help prevent complications and ensure the safety of the patient.
IX. Interactions with Sumatriptan
Drug-Drug Interactions
Sumatriptan has the potential to interact with medications, which could result in significant effects. For example, if you combine Sumatriptan with triptans or ergotamines, there may be an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. Additionally, if you take Sumatriptan while using SSRIs or SNRIs, it could also elevate the risk of serotonin syndrome. Moreover, if you are concurrently using MAO inhibitors, it can cause increased levels of Sumatriptan in your body.
Drug-Food Interactions
Although Sumatriptan typically does not interact with food, it is advisable for patients to follow the prescribed instructions and take the medication with or without food.
Drug-Alcohol Interactions
Drinking alcohol can worsen Sumatriptan's side effects, like feeling dizzy or drowsy. It's advised that patients refrain from consuming alcohol while using this medication.
X. Warnings and Precautions
Cardiovascular Risks
Sumatriptan has the potential to bring about variations in blood pressure and could be risky for individuals with cardiovascular issues. It is essential to evaluate the following factors; Whether there is a history of heart attacks or strokes, The presence of angina, or any other indications of artery disease, If hypertension is under control.
Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome, a condition that can be life-threatening, may arise when using Sumatriptan in combination with medications that affect serotonin levels.
Overuse and Rebound Headaches
Using Sumatriptan excessively can result in medication overuse headaches. Rebound headaches that may be more intense and occur more frequently. It is essential to monitor your usage.
XI. Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
Sumatriptan should not be used by individuals who have a history of heart disease or stroke, uncontrolled blood pressure or hemiplegic or basilar migraines.
Relative Contraindications
Some situations where caution should be exercised may involve individuals, with; managed high blood pressure Serious liver damage.
XII. Careful Administration of Sumatriptan
Monitoring Parameters
Regularly monitoring aspects of your health is crucial, including; 1. You are keeping track of your blood pressure. 2. Pay attention to your heart rate and rhythm. 3. Being aware of any signs or symptoms related to serotonin syndrome. Taking these measures helps ensure you stay proactive in maintaining health and well-being.
Patient Education and Counseling Points
Patients should be informed about the usage of Sumatriptan as directed by their healthcare provider. Additionally, they should remain vigilant for any side effects and promptly seek medical attention if they experience severe symptoms such as chest pain or intense abdominal pain.
XIII. Important Precautions with Sumatriptan
Allergic Reactions
It is essential for individuals using Sumatriptan to be informed that if they notice any symptoms of a reaction, such as the presence of hives, breathing difficulties, or swelling in the face, lips, or tongue, they should discontinue taking the medication and promptly seek medical assistance.
Use in Patients with Liver or Kidney Disease
Patients who have liver or kidney problems may require changes, in their dosage and it is essential to closely monitor them in such situations.
XIV. Administration to Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Older individuals may have a vulnerability to the potential adverse reactions of Sumatriptan, particularly those associated with blood pressure and cardiac well-being.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Sumatriptan may be used during pregnancy if the potential benefits outweigh the risks. Nursing mothers must be cautious, as Sumatriptan can pass into breast milk.
Administration to Children: Safety and Efficacy
The use of Sumatriptan in patients has not been definitively established for its safety and effectiveness. Therefore caution should be exercised when administering it to this population.
XV. Overdosage of Sumatriptan
Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Signs that may indicate an overdose of Sumatriptan include; Experiencing tremors or shaking, Noticing red or flushed skin, Having difficulty breathing Losing consciousness. Please seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
Management and Treatment Options
The treatment for an overdose mainly involves providing support and immediate medical attention. It is crucial to monitor vital signs and carefully watch the patient.
XVI. Storage Conditions for Sumatriptan
Recommended Storage Temperature
It would be best if you kept Sumatriptan in a place where the temperature's around 20 to 25°C (68 to 77°F).
Protection from Light and Moisture
It's important to keep medications in their packaging away from too much moisture and direct sunlight. This helps maintain their effectiveness and safety.
XVII. Handling Precautions
Safe Handling Practices
When using Sumatriptan it's essential to handle it with hands and make sure not to touch the medication to your eyes or any other sensitive areas.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Ensure you follow the guidelines from your pharmacy or local waste disposal facility to dispose of any expired Sumatriptan properly. This is important to ensure it doesn't pose any risks to others.