Sumatriptan
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Sumatriptan
- III. Uses of Sumatriptan
- IX. Interactions of Sumatriptan
- X. Important Precautions with Sumatriptan
- XI. Contraindications of Sumatriptan
- XII. Warning for Sumatriptan Users
- XIII. Special Administration Considerations
- XIV. Overdosage of Sumatriptan
- XV. Storage of Sumatriptan
- XVI. Handling Precautions for Sumatriptan
- XVII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
A. Sumatriptan Background
Sumatriptan is a medication known for successfully treating migraines and cluster headaches. It is a selective serotonin receptor agonist first developed in the late 1980s. Since then, it has become essential in alleviating the debilitating symptoms experienced by numerous worldwide suffering from these neurological conditions. This article aims to provide detailed information on Sumatriptans' composition, uses, and effectiveness.
B. Article Overview
This article offers a comprehensive examination of Sumatriptan, focusing on its composition - including its primary constituents and inactive ingredients - as well as its approved uses. It also explores the drug's efficacy in treating specific conditions and discusses the duration and onset of its effectiveness.
II. Composition of Sumatriptan
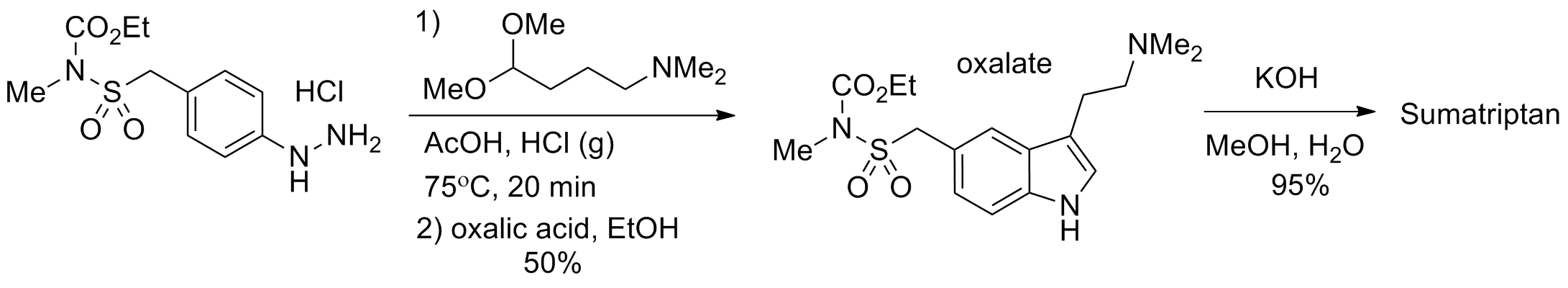
A. Primary Constituents
The main component of Sumatriptan that contributes to its effectiveness is the compound. This potent and selective agonist of the five hydroxytryptamine1 (5 HT1) receptor subtype specifically targets the neurological pathways associated with migraine and cluster headaches. Its ergoline structure enables it to bind to these receptors, constricting cranial blood vessels and inhibiting pro-inflammatory neuropeptide release.1
B. Inactive Ingredients
Alongside the active ingredient in Sumatriptan formulations, various inactive ingredients are included, which can differ depending on the specific manufacturer and type of formulation. Despite being fixed, these additional components, such as lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, and magnesium stearate, serve as binders, fillers, and lubricants. These components are crucial for ensuring the drug's stability, appearance, and overall effectiveness in delivery.2
References:
- "Mechanisms of the 5-HT1 receptor agonists' actions in migraine," Neuroscience in the 21st Century
- "Sumatriptan - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses," Drugs.com
III. Uses of Sumatriptan
A. Approved Uses
Sumatriptan has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for managing acute migraine attacks in adults, with or without aura. It has also been approved for the treatment of acute cluster headache episodes. It is important to note that Sumatriptan is not recommended for use in preventing migraines or managing hemiplegic or basilar migraines.1
B. Effectiveness in Treating Specific Conditions
The effectiveness of Sumatriptan in treating migraines and cluster headaches cannot be disputed. The drug works by acting on specific serotonin receptors (5 HT1) found in blood vessels in the brain. Activation of these receptors causes vasoconstriction, which leads to relief from migraine and cluster headache symptoms.2
C. Duration and Onset of Effectiveness
Sumatriptan typically starts working quickly, with peak plasma concentrations reached within 10 to 50 minutes after taking it orally. The drug's effects usually begin relatively shortly after ingestion, with an average half-life of about two hours. However. Individual differences in physiology can affect these timeframes. As is the case with most pharmaceutical agents.3
References:
- "Sumatriptan - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses," Drugs.com
- "Sumatriptan: A Review of its Use in the Treatment of Migraine and Cluster Headache," Journal of Pain and Symptom Management
- "Sumatriptan," LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury
IX. Interactions of Sumatriptan
A. Potential Drug Interactions
When using Sumatriptan, being aware of potential interactions with other medications is essential. Taking ergotamine-containing or ergot-type medications alongside Sumatriptan can result in prolonged vasospastic reactions. Additionally, the concurrent use of MAO-A inhibitors, sometimes prescribed for depression, is contraindicated due to an increased risk of serotonergic syndrome. Certain medications used to treat depression and anxiety disorders, such as SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) or SNRIs (serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors), can also interact with Sumatriptan. This interaction may lead to a condition known as serotonin syndrome, which can cause symptoms like restlessness, hallucinations, rapid heartbeat, fever, loss of coordination, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.1
B. Food and Lifestyle Interactions
While there have been no direct documented food interactions with Sumatriptan, it is essential to consider how lifestyle choices can impact migraine symptoms and treatment effectiveness. Consuming alcohol while taking Sumatriptan can worsen migraine headaches and intensify side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating. Additionally, dietary habits like skipping meals or dehydration can trigger migraines and increase the need for Sumatriptan. To successfully manage migraines. It is crucial to maintain a balanced diet and have regular meal times. Stay adequately hydrated. And make overall healthy lifestyle choices.2
References:
- "Sumatriptan - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses," Drugs.com
- "Diet and Headache: Part 1," Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain
X. Important Precautions with Sumatriptan
A. Avoidance in Specific Health Conditions
Sumatriptan should be used cautiously in specific populations with an increased risk of experiencing adverse effects. These individuals include those with coronary artery disease (CAD), Prinzmetals' angina, or other significant underlying cardiovascular conditions. Patients with uncontrolled hypertension, severe hepatic impairment, or a history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) may also face risks when using this medication. Therefore, reviewing the patient's medical history and considering potential alternative treatments in these cases is essential.1
B. Precautions for Long-Term Use
While Sumatriptan can provide relief during acute migraine attacks, it is essential to exercise caution when using it for long-term management. Misuse or overuse of Sumatriptan can result in medication overuse headaches, which ironically can increase the frequency of migraines. Furthermore. Relying heavily on this drug over an extended period can potentially lead to dependency. Intensify side effects. And increase the likelihood of drug interactions. Consequently, individuals who suffer from persistent migraines are encouraged to consult their healthcare provider for a comprehensive and sustainable migraine management plan that best suits their needs.2
References:
- "Sumatriptan - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses," Drugs.com
- "Medication Overuse Headache," National Headache Foundation
XI. Contraindications of Sumatriptan

A. Health Conditions that Prohibit Use
Certain health conditions may make it unsafe to use Sumatriptan, as the potential benefits might not outweigh the risks. For instance. Individuals with a history of coronary artery disease (CAD). Prinzmetals angina or other significant underlying cardiovascular conditions should not take Sumatriptan. Likewise, patients with uncontrolled hypertension, severe hepatic impairment, or a history of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) should avoid using Sumatriptan.1
B. Medications that Interact Dangerously
Specific medications can dangerously interact with Sumatriptan and cause severe adverse reactions. For example, when taken together with Monoamine oxidase A inhibitors (MAO-A inhibitors), there is an increased risk of developing serotonin syndrome. This condition can be life-threatening, characterized by symptoms such as agitation, hallucinations, rapid heartbeat, and fever. Similarly, if Sumatriptan is co-administered with other 5 HT1 agonists or ergotamine-containing medications, it can result in cumulative vasoconstrictive effects. Therefore it is best to avoid combining these medications.2
References:
- "Sumatriptan - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses," Drugs.com
- "Sumatriptan: medicine to treat migraines and cluster headaches," NHS
XII. Warning for Sumatriptan Users
A. Risks Associated with Improper Use
Improper use of Sumatriptan can have severe consequences for one's health. This includes the potential for medication overuse headaches, a paradoxical reaction that can increase the frequency of migraines. In addition, taking Sumatriptan in combination with certain other medications can contribute to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. Therefore it is essential to utilize this medication only under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional.
B. Dangers of Overdose and Misuse
Misusing or overdosing on Sumatriptan can result in numerous harmful effects. Aside from increasing the risk of experiencing side effects typically associated with the medication. An overdose can lead to symptoms such as convulsions, tremors, and paralysis. Furthermore, it can cause high blood pressure, an unusually slow or rapid heart rate, or even trigger a heart attack in severe cases. For this reason, it is crucial to strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage to ensure safe usage of this medication.
XIII. Special Administration Considerations
A. Administration to the Elderly
The administration of Sumatriptan to elderly individuals should be cautiously approached due to the potential increased risk of cardiovascular side effects. This is because the physiological functions of the body alter with age. They are making elderly individuals more likely to have pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. It may be necessary for healthcare providers to consider alternative treatment options for this population.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety of using Sumatriptan in pregnant women and nursing mothers has not been definitively established. At the same time, animal studies have shown adverse effects on the fetus. There is a lack of adequate and well-controlled studies in humans. Therefore. Healthcare providers should only prescribe Sumatriptan during pregnancy if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Nursing mothers should also exercise caution as it is unclear whether Sumatriptan is excreted in human milk.
C. Administration to Children
The safety and effectiveness of Sumatriptan in pediatric populations have not been unquestionably confirmed. Though some research has been conducted, further comprehensive studies are needed. Hence. Healthcare providers should approach the use of Sumatriptan in children with caution and ensure close supervision by a healthcare provider
XIV. Overdosage of Sumatriptan
A. Symptoms of Overdosage
Overdosing on Sumatriptan can lead to a range of harmful symptoms. In more severe cases, patients may experience significant physical distress, including hypertensive crises, rapid heartbeat, seizures, and tremors. Symptoms resembling a stroke may be present, such as changes in vision, confusion, or difficulty speaking if suspected of an overdose. Obtaining immediate medical attention is essential.
B. Emergency Treatment and Procedures
When a Sumatriptan overdose occurs, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. The typical treatment involves stopping the administration of the drug and providing supportive care. In certain situations, hospitalization and monitoring of vital signs might be necessary. Since no specific antidote for Sumatriptan is available, Treatment primarily focuses on managing symptoms and providing support to the patient.
XV. Storage of Sumatriptan
A. Recommended Storage Conditions
It is of utmost importance to store Sumatriptan properly to maintain its effectiveness. To achieve this, the medication should be kept in its original packaging at room temperature, away from light and moisture. It is essential to avoid exposing the drug to extreme temperatures, such as those commonly present in bathrooms or cars, as this may result in a loss of efficacy.
B. Handling and Disposal Guidelines
When it comes to handling and disposing of unneeded medications. We must take extra precautions to ensure the safety of pets, children, and other individuals. It is advised not to flush unused Sumatriptan down the toilet or pour it into a drain unless specifically instructed. Instead, we encourage you to use medicine take-back programs or follow any specific disposal guidelines provided on the drug label.
XVI. Handling Precautions for Sumatriptan
When handling Sumatriptan, there are a few basic precautions to remember. It's important to always wash your hands before and after taking the medication. Additionally, store the drug where children and pets cannot reach it. It's also crucial not to share Sumatriptan with others, even if they have similar symptoms. In the event of accidental exposure, such as getting Sumatriptan in your eyes or skin. Make sure to wash the affected area with water thoroughly. If you experience any adverse reactions or accidentally ingest Sumatriptan. Seek immediate medical attention.
XVII. Conclusion
In conclusion, this extensive examination of Sumatriptan has shed light on its composition, critical uses, potential side effects, and interactions. It has also presented imperative information regarding proper storage, careful management, and safe disposal methods. Although the efficacy of Sumatriptan in treating migraines and cluster headaches is undeniable; its usage should be prudently approached and authorized by a diligent healthcare provider to optimize clinical benefits as well as safeguard patient welfare
2 . Important information about Imitrex Sumatriptan
3 . Points to Consider Before Using Imitrex Sumatriptan
4 . Adverse reactions of Imitrex Sumatriptan
5 . Dosage related Instruction about Imitrex Sumatriptan
6 . Can Imitrex Sumatriptan Be Used By All?
7 . Imitrex Sumatriptan - Its mode of Action and Effects
8 . How to Use Imitrex Safely?
9 . Safety Measures Required For Using Generic Imitrex Sumatriptan
10 . Imitrex Sumatriptan - Its mode of Action and Effects
11 . How to Use Imitrex Sumatriptan Safe and Sound?
12 . Safety Measures Required For Using Generic Imitrex Sumatriptan
13 . Medical Alerts Related to Imitrex Sumatriptan
14 . Proven Researches Related To Effectiveness of Imitrex Sumatriptan in Treating Migraine Headache