Twinrix Syringe
- I. Introduction to Twinrix Syringe
- II. Uses of Twinrix Syringe
- III. Off-Label Uses of Twinrix Syringe
- IV. How Twinrix Syringe Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition of Twinrix Syringe
- VII. Twinrix vaccine side effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects of Twinrix Syringe
- IX. Interaction of Twinrix Syringe with Other Medications
- X. Warnings and Precautions
- XI. Contraindications of Twinrix Syringe
- XII. Important Precautions When Administering Twinrix Syringe
- XIII. Careful Administration Guidelines
- XIV. Administration to Elderly Patients
- XV. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- XVI. Administration to Children and Adolescents
- XVII. Overdose of Twinrix Syringe
- XVIII. Storage of Twinrix Syringe
- XIX. Handling Precautions for Twinrix Syringe
I. Introduction to Twinrix Syringe
Overview of Twinrix Syringe
The Twinrix Syringe is a vaccine that helps protect against both Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B infections by combining Hepatitis A virus and recombinant Hepatitis B surface antigen in one shot given through a muscle injection mainly for people needing protection, against both diseases at the same time.
Importance of Vaccination Against Hepatitis A and B
Serious liver infections, like Hepatitis A and B are caused by viruses – Hepatitis A is usually spread through food and water sources while Hepatitis B is commonly transmitted through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. Vaccination stands out as the approach to ward off these illnesses that may result in long term liver complications such, as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Types of Hepatitis A and B Vaccines
Hepatitis A and B vaccines can be acquired separately; however, Twinrix provides a combined option that protects against both viruses in one shot, making it ideal for travelers and healthcare workers who require coverage for both.
Who Should Receive Twinrix?
Twinrix is suggested for people who might be exposed to both Hepatitis A and B viruses, such as travelers to regions where these diseases are common, healthcare workers who may encounter contaminated fluids, and individuals with ongoing liver issues.Immunocompromised individuals and those involved in activities with risks could also find it beneficial to get the Twinrix vaccination.
II. Uses of Twinrix Syringe
Prevention of Hepatitis A
Prevention of Hepatitis B
In addition to protection from Hepatitis A, Twinrix provides immunity against Hepatitis B. The vaccine includes a recombinant Hepatitis B surface antigen, stimulating an immune response to guard against future infection.
Indications for Travelers to High-Risk Areas
Twinrix can be really helpful, for people traveling to areas where Hepatitis A and B're concerns in many developing countries with higher rates of these viruses; getting vaccinated becomes a crucial precaution, for travelers.
Recommended Use for Healthcare Workers
Healthcare professionals encounter contaminated fluids which exposes them to a heightened risk of contracting Hepatitis B infection; Twinrix is advised for their dual safeguard, against this disease to enable them to operate securely within healthcare settings.
Use in Immunocompromised Patients
People with weakened systems, such as those with HIV or receiving treatments that suppress the system, are more susceptible to infections like Hepatitis A and B. Twinrix provides safeguarding for these at-risk groups.
III. Off-Label Uses of Twinrix Syringe
Potential Off-Label Use for Hepatitis A/B Combined Vaccination in At-Risk Populations
Although not formally classified by authorities, Twinrix could be used for purposes beyond its scope of intent, especially for groups with a high risk of contracting both Hepatitis A and B through behaviors that put them at risk or residing in tight-knit communities that are prone to outbreaks.
Considerations in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
People who have long-term liver issues, like cirrhosis or hepatitis C could find Twinrix in avoiding liver infections such as Hepatitis A or B and lowering the chances of severe complications that could be life-threatening.
Use in Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis for Certain Occupational Groups
Some professions, like lab technicians or emergency medical technicians, might need to take Twinrix before coming into contact with people with Hepatitis A or B in their line of work to stay safe from exposure.
IV. How Twinrix Syringe Works
Mechanism of Action: Immune Response to Hepatitis A and B Antigens
Twinrix works by inducing an immune response through the introduction of viral antigens. Upon vaccination, the body identifies these harmless components as foreign invaders and produces specific antibodies to target them.
Role of Inactivated Hepatitis A Virus in Protection
The Hepatitis A virus in Twinrix is unable to cause illness as it is deactivated; however, it does prompt the system to identify and deactivate the live virus if it is ever encountered again in the future.
Role of Recombinant Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Protection
The Hepatitis B part of Twinrix contains a surface antigen that imitates the virus to help the immune system build a defense and keep it in memory, for lasting protection.
Immune System Activation and Long-Term Protection
Twinrix triggers a reaction that results in the creation of long-lasting antibodies. Measures like these help people protect against both Hepatitis A and B over time.
Twinrix effectiveness after 1 dose
Studies revealed that when it comes to hepatitis A vaccination results, 94 percent of adults had antibodies and after the dose; this number rose to 99. percent following the dose and reached a full 100 percent after the third dose was administered.
V. Dosage and Administration
Twinrix schedule
Most adults get the Twinrix vaccine in three doses: the first dose is given, followed by a dose after a month and a third dose after six months.
Dosing Guidelines for Children and Adolescents
For kids and teens between 1 and 18 years old, they typically receive three doses spread out across six months, which is similar to how adults are dosed. The medications made for children may have potency levels.
Special Dosing Considerations for Immunocompromised Individuals
Patients, with weakened systems might need doses or a different vaccination schedule to ensure a strong immune response is achieved. In situations where necessary giving booster shots is advised.
Missed Dose and What to Do
If a dose of Twinrix is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible. Delaying a dose may reduce the vaccine's overall effectiveness, but restarting the series is typically unnecessary.
Administration Technique: Syringe Handling and Injection Site
Twinrix is given through a shot, into the deltoid muscle. It's important to handle the syringe to maintain sterility while keeping an eye on the injection site for any negative reactions.
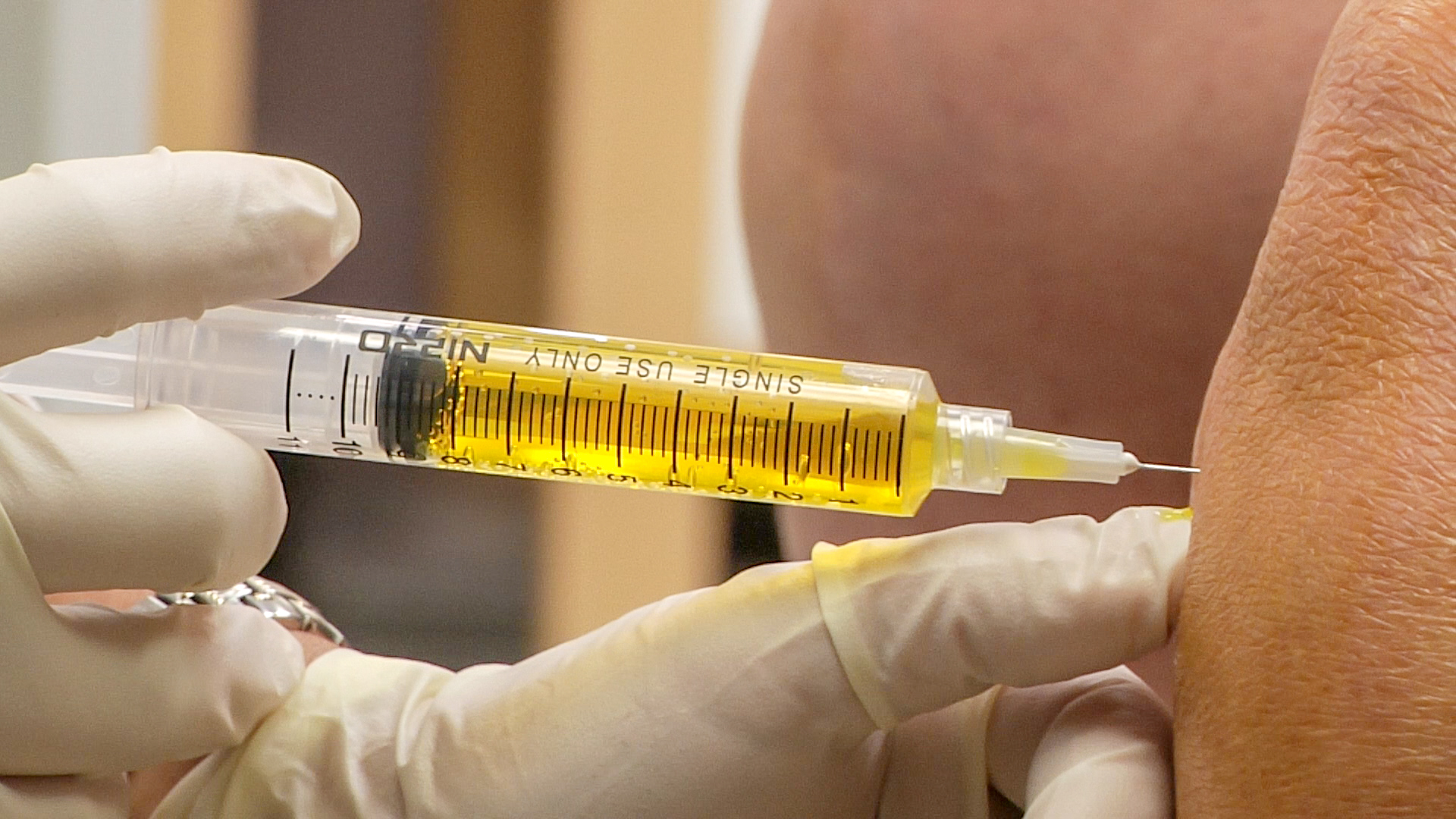
Minimum interval between twinrix dose 2 and 3
The typical dosage for TWINRIX involves receiving three vaccine doses spread out over a period of six months.
VI. Composition of Twinrix Syringe
Breakdown of Active Ingredients (Hepatitis A Inactivated Virus and Hepatitis B Recombinant Antigen)
Twinrix consists of two elements. Deactivated Hepatitis A virus and engineered Hepatitis B surface antigen collaborate to offer complete safeguard against both viruses.
List of Excipients and Preservatives
Twinrix contains excipients, like aluminum hydroxide that help boost the response, as an trace amounts of formaldehyde and neomycin used in the production process.
Role of Each Component in the Vaccine
Every part of the vaccine serves a purpose, from the antigens that prompt an immune reaction to the adjuvants that help guarantee the vaccine's efficacy.
Formulation Strengths
Twinrix comes in versions designed for adults and children, with levels of the components customized based on the individual's age and immune needs.
VII. Twinrix vaccine side effects
Overview of Potential Side Effects
Like all vaccines, Twinrix can cause side effects. These are typically mild and transient, resolving within a few days. However, some individuals may experience more serious reactions.
Common Side Effects: Localized Reactions at Injection Site
Reported side effects of the injection include localized reactions, like pain and redness, at the site of injection; typically these symptoms fade away quickly without needing any intervention.
Systemic Reactions: Fever, Fatigue, Muscle Aches
Potential adverse reactions might consist of symptoms such as an increase in body temperature or feeling tired and achy in the muscles after receiving the vaccine; these are typically indicative of the system's reaction and are usually not severe.
Rare but Serious Side Effects: Severe Allergic Reactions, Neurological Disorders
Rare severe adverse effects may arise, like anaphylaxis or neurological issues, like Guillain Barré syndrome, although these occurrences are rare and call for medical intervention.
Reporting of Side Effects and Importance of Monitoring
Report any reactions to your healthcare provider promptly to guarantee safety and the effectiveness of the vaccine. Monitor for side effects post-vaccination.
VIII. Common Side Effects of Twinrix Syringe
Pain, Redness, and Swelling at Injection Site
It's normal to experience pain and swelling at the injection site after getting the vaccine – these reactions usually don't last long. Are nothing to worry about.
Fever and General Discomfort
After getting the Twinrix vaccine, you may experience a fever and overall unease; however, these symptoms typically go away within 48 hours without requiring any treatment.
Headache and Nausea
A few people might experience headaches or nausea after getting vaccinated. These effects are usually not severe and tend to disappear after a couple of days.
Muscle Pain (Myalgia)
Another usual side effect is muscle soreness in the arms and shoulders; however, it can generally be alleviated with over-the-counter pain medications.
Fatigue Following Vaccination
Feeling tired or exhausted can sometimes happen after getting the Twinrix vaccine but don't worry. It's just temporary. Should go away in a day or two.
IX. Interaction of Twinrix Syringe with Other Medications
Potential Drug Interactions: Immunosuppressants and Twinrix Efficacy
Patients taking drugs may lower the effectiveness of Twinrix by weakening the body's response, so it is advisable for them to discuss the timing of their vaccine with their healthcare provider.
Interaction with Other Vaccines
Twinrix can be given along with vaccines; however, it is important to use syringes and injection spots for each vaccine administered simultaneously with it.
Effects on Live Vaccines When Co-administered
When Twinrix is given together with vaccines it may affect the bodys capacity to produce an immune response. It is advised to separate vaccines from Twinrix by least four weeks.
Some antiviral drugs may affect how well the Twinrix vaccine works against Hepatitis B. Before getting vaccinated, Make sure to let your healthcare provider know if you're taking any medications.
X. Warnings and Precautions
Warnings for Individuals with Severe Allergic Reactions
Patients who have previously had reactions to any ingredient in the Twinrix Syringe should not be administered this vaccine under any circumstances. It can lead to immediate hypersensitivity reactions, like anaphylaxis, that demand prompt medical intervention. Utmost caution is advised if such reactions have been documented in a patient's medical records.
Special Considerations for Immunocompromised Patients
Individuals with weakened systems due to factors like chemotherapy or advanced HIV may show a response to the vaccine effects. While the use of Twinrix is not officially discouraged in cases the effectiveness of the vaccine could be lower potentially requiring booster shots or closer monitoring.
Risks for Patients with Bleeding Disorders or on Anticoagulants
People who have bleeding conditions, like hemophilia or are taking blood thinners are more likely to develop hematomas after getting an injection, in the muscle area. To reduce the risk of bleeding in situations advised to give the vaccine under care and take precautions by putting pressure on the injection spot.
Monitoring for Severe Reactions After Administration
Healthcare professionals need to monitor patients for a minimum of 15 minutes following vaccination to catch any signs of severe allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis, that may require immediate treatment with epinephrine and supportive measures despite being uncommon occurrences.
XI. Contraindications of Twinrix Syringe
Absolute Contraindications: Severe Allergic Reaction to Any Component
Those who have had a reaction (like anaphylaxis) either to a component of Twinrix or a prior dose of the Hepatitis A or B vaccine should not be given Twinrix at all costs due to the absolute contraindications associated with it.
Contraindication in Patients with History of Hepatitis A/B Vaccine Hypersensitivity
Patients with a known history of hypersensitivity to any Hepatitis A or B vaccine should avoid receiving Twinrix. In such cases, alternative vaccination options or strict monitoring may be necessary.
Contraindications for Use in Individuals with Acute Illness
Twinrix administration should be deferred in individuals suffering from acute, moderate to severe illness, with or without fever. Vaccination can be rescheduled once the individual has recovered to avoid complications or misinterpretation of vaccine-related adverse events.
XII. Important Precautions When Administering Twinrix Syringe
Precautions for Individuals with Pre-existing Medical Conditions
Healthcare providers should carefully evaluate individuals, with existing health issues, like disorders and long term illnesses before deciding on vaccination to weigh the pros and cons in these scenarios.
Monitoring for Anaphylaxis and Severe Allergic Reactions
Following the procedure, note any signs of anaphylaxis in patients post-administration, such as breathing difficulties, swelling in the face or throat, and hives.It is crucial to have epinephrine and other emergency measures easily accessible during the process.
Considerations for Patients with Neurological Disorders
Individuals who have existing conditions, like sclerosis or a past bout with Guillain Barré syndrome, should undergo a medical assessment before getting the Twinrix vaccine as a precautionary measure advised by healthcare professionals to ensure personalized care due to the small chance of worsening neurological issues despite the overall safety profile of the vaccine.
Precautionary Measures for Handling and Storage of the Syringe
To maintain its efficacy, the Twinrix Syringe must be handled and stored under strict conditions. This includes avoiding exposure to freezing temperatures, direct sunlight, or excessive heat, all of which may degrade the vaccine's potency.
XIII. Careful Administration Guidelines
Administering Twinrix to Patients with Autoimmune Diseases
Individuals with disorders like lupuѕ or rheumatoid arthritis may need guidance before getting the Twinrix vaccine. Due to changes in response, you might need doses even though the vaccine itself usually doesn't pose much risk.
Guidelines for Patients with Kidney or Liver Disease
People with long-term kidney or liver issues may be prescribed the Twinrix vaccine. Need monitoring is crucial—particularly for those awaiting liver transplants or undergoing dialysis treatment. It's important to consult a healthcare professional before getting vaccinated to guarantee protection.
Management of Patients with History of Seizures or Epilepsy
People who have had seizures or epilepsy in the past might be prescribed the Twinrix vaccine; however, medical professionals need to consider any factors that could lead to vaccination fever or other side effects that may worsen seizure episodes.
Careful Administration for Those with Egg or Yeast Allergies
Individuals who are allergic to yeast, should be assessed before receiving Twinrix since the vaccine contains components derived from yeast even though it does not include egg protein in its formulation.
XIV. Administration to Elderly Patients
Effectiveness and Safety of Twinrix in Elderly Patients
As people age, their immune systems may not work well, and older individuals might not respond strongly to vaccines as younger people do. Twinrix has proven to be effective in this group; however, extra doses or booster shots might be needed for protection against diseases.
Dosage Adjustments for Elderly Populations
Elderly patients do not require dosage changes; however it is crucial to take into account their health and any existing medical conditions when giving them the vaccine. Vigilantly watching for any reactions is especially vital for this demographic.
Considerations for Immunosenescence and Immune Response in the Elderly
As people grow older and their immune system weakens (known as immunosenescence), it might affect how well they respond to the Twinrix vaccine intended to protect them against diseases like Hepatitis A and B. To ensure protection, against these diseases in the population doctors may recommend extra doses of the vaccine or different vaccination approaches.
Monitoring for Adverse Reactions in Geriatric Patients
Adverse reactions such as fatigue, muscle pain, and fever should be monitored closely in elderly patients, as these side effects may exacerbate existing conditions or contribute to frailty.
XV. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety Profile of Twinrix During Pregnancy
Clinical trials have not conclusively established Twinrix's safety during pregnancy. Therefore, it should be administered only if the potential benefits outweigh the risks, particularly for women at high risk of exposure to Hepatitis A and B.
Considerations for Administration to Nursing Mothers
Breastfeeding mothers can usually get the Twinrix vaccine without worrying about passing its components through breast milk to their babies; however it's advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure the well being of both the mother and child.
Effects on Fetus and Newborns
While no definitive studies have shown the harmful effects of Twinrix on fetuses or newborns, the decision to vaccinate pregnant or nursing women should consider the motherâs risk of exposure and potential transmission of Hepatitis A or B.
Recommendations for Vaccination in High-Risk Pregnant Women
Expectant mothers who are, at a heightened risk of acquiring Hepatitis A or B. Such as individuals working in healthcare or those journeying to regions with high infection rates. Might be recommended to receive Twinrix if the possible advantages outweigh the hazards.
XVI. Administration to Children and Adolescents
Pediatric Dosing Guidelines
Twinrix is given to kids and teens in three doses with grown-ups; still, the amount might change depending on the child's age and weight.
Age Restrictions and Recommendations for Use in Children
Twinrix is usually recommended for children who are at least one year old. Babies under the age of one might need other vaccination approaches since their immune systems may not react effectively to the vaccine.
Safety and Efficacy in Pediatric Populations
The vaccine has proven to be safe and effective for children, with temporary side effects resembling those seen in adults.
Co-administration of Twinrix with Other Childhood Vaccines
Twinrix can be co-administered with other routine childhood vaccines, such as the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine. Using separate syringes and injection sites when administering multiple vaccines is important.
XVII. Overdose of Twinrix Syringe
Symptoms of Overdose and Emergency Protocols
Though rare occurrences, vaccine overdoses can happen if the dosing schedule is accidentally repeated or mishandled. Signs of an overdose may manifest as heightened localized responses, such, as swelling along with symptoms, like fever or fatigue.
Immediate Steps Following Overdose
In the event of an overdose, the individual should be monitored for any adverse reactions. Supportive care is usually sufficient, and no specific antidote is required for vaccine overdoses.
Monitoring and Supportive Treatment for Overdose Cases
Patients who have overdosed must be carefully observed for any indications of reactions, like responses. Typically, providing care such as pain relief and fever management should be adequate.
Reporting of Overdose Incidents to Healthcare Providers
In case of an overdose, it is important to notify healthcare professionals and the appropriate public health agencies about the incident for documentation purposes, as this can contribute insights for shaping recommendations and protocols.
XVIII. Storage of Twinrix Syringe
Recommended Storage Conditions for Twinrix
Twinrix needs to be stored between 2°C and 8°C to maintain its effectiveness. It should not be frozen, as this can impact the vaccine's potency.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
The expiration date of Twinrix is usually stated on the packaging. It is important not to use it after that date has passed as expired vaccines may not work effectively and could cause harm.
Proper Handling of Syringe Before Use
Make sure to shake the syringe before using it to ensure that the vaccine components are well mixed and properly suspended in it! Healthcare providers need to check the vaccine for any signs of particles or unusual coloration as this could signal that it might have gone bad or spoiled.
Importance of Cold Chain Maintenance
Preserving the vaccine's effectiveness relies heavily on keeping the chain intact all the way from manufacturing to the point of administration. If there's a disruption in the chain, such as prolonged exposure to room temperature, it could impact the potency of the vaccine.
XIX. Handling Precautions for Twinrix Syringe
Guidelines for Proper Syringe Handling
Healthcare professionals need to handle the syringe to prevent contamination. They should always practice a sterile technique to ensure that the needle and syringe remain unexposed to unsanitary surfaces.
Safe Disposal of Used Syringes
Used syringes should be disposed of in designated sharps containers to prevent accidental needle sticks or contamination. Proper disposal is essential to maintaining infection control standards in healthcare settings.
Infection Control Measures
Healthcare professionals administering the vaccine need to adhere to infection control guidelines, such as practicing hand hygiene and wearing gloves while using sterilized equipment, to reduce the chances of cross-contamination and the spread of infections.
Avoiding Contamination and Maintaining Sterility
It's really important to keep things clean when giving someone Twinrix shots. You shouldn't reuse the syringe and clean the injection spot before giving the shot to keep patients safe and ensure the vaccine works well.
Twinrix Syringe FAQ
- What is a Twinrix vaccine syringe?
- How do you administer twinrix vaccine?
- Is TWINRIX one shot?
- Is TWINRIX an intramuscular injection?
- How many years is TWINRIX good for?
- Does TWINRIX need to be refrigerated?
- Is TWINRIX safe?
- Is TWINRIX a prefilled syringe?
- How to inject TWINRIX?
- How many mL is a TWINRIX shot?
- Is one shot of TWINRIX enough?
- Do you need a prescription for TWINRIX?
- How fast does TWINRIX work?
- Should TWINRIX be cloudy?
- Who is TWINRIX recommended for?
What is a Twinrix vaccine syringe?
Twinrix Adult vaccine is offered in both a 1-milliliter vial and a 1 milliliter prefilled syringe for injection administration. It comprises inactivated hepatitis A viruses and components of the hepatitis B virus.
How do you administer twinrix vaccine?
Your doctor will administer TWINRIX through an injection in your arm or the front of the thigh for childrens vaccinations schedule: first dose, second dose after a month and third dose after six months from the initial dose for those aged 19 years and above.
Is TWINRIX one shot?
TWINRIX is typically administered in three vaccine doses spread out over six months with the flexibility to select the date for the placement at your convenience followed by the second dose one month later and concluding with the final dose six months after the first administration date for standard dosing procedures in adults aged 19 and above while an alternative rapid four-dose schedule option is also accessible, for this age group.
Is TWINRIX an intramuscular injection?
TWINRIX is given through a shot in the muscle by a healthcare provider.
How many years is TWINRIX good for?
You can expect protection for around 20 years against hepatitis A and lifelong immunity for hepatitis B.
Does TWINRIX need to be refrigerated?
Make sure to keep Twinrix in the fridge at a temperature between 35°F and 46°F, with a target of around 40°F.
Is TWINRIX safe?
The side effects of the Twinrix vaccine are typically mild and transient; they commonly consist of symptoms such as redness or swelling at the injection site and feelings of fatigue or irritability that usually subside within a day.
Is TWINRIX a prefilled syringe?
TWINRIX is available in prefilled syringes containing a slightly milky liquid mixture comprising the killed hepatitis A virus and the surface protein of the hepatitis B virus derived from engineered yeast cells. The vaccine is safe and noninfectious; it does not cause hepatitis A or hepatitis B infections.
How to inject TWINRIX?
Attach a needle to the filled syringe and give the injection into the muscle tissue in the arm area known as the deltoid region using a 1 mL dose of TWINRIX only. Inject carefully and avoid injecting in the buttocks as doing so may lead to an ineffective reaction.
How many mL is a TWINRIX shot?
The typical dosing plan includes 3 doses (each of 2 mL) administered through injection into the muscles at intervals of 0 months apart initially and at 6 months later on average. To speed up the process one could opt for a schedule involving four doses (each of size ml) administered via injection on Days starting from Day O followed by Day after a week and lastly Days in the range of 21 to 30, with an additional booster dose given in the twelfth month.
Is one shot of TWINRIX enough?
Twinrix will not provide you with enough immunity to protect you for your trip
Do you need a prescription for TWINRIX?
The usual injections prescribed are for conditions like shingles and for travel purposes, like the Twinrix vaccine (for Hepatitis A and B).
How fast does TWINRIX work?
After the dose 95 percent of individuals are shielded from hepatitis A and B within a month.
Should TWINRIX be cloudy?
If the vaccine looks like a white mixture and is not transparent in appearance, it is good to go for use.
Who is TWINRIX recommended for?
Twinrix is recommended for vaccinating individuals aged 18 and above against hepatitis A and B infections.