Genevac-B Injection
- Introduction to Genevac-B Injection
- Uses of Genevac-B Injection
- Composition of Genevac-B Injection
- How Genevac-B Injection Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Storage and Handling of Genevac-B Injection
- Side Effects of Genevac-B Injection
- Precautions and Warnings
- Contraindications
- Interactions with Other Medications or Vaccines
- Administration to Specific Populations
- Careful Administration Guidelines
- Overdosage and Management
- Handling Precautions
Introduction to Genevac-B Injection
Overview of Genevac-B Injection
Genevac B Injection is a vaccine created to prevent Hepatitis B infection utilizing cutting-edge biotechnology to boost the body's system efficiently and effectively, making it a crucial component of global public health efforts due to its proven safety and effectiveness.
Importance and Role of Genevac-B in Medical Treatment
Vaccines are crucial in lessening the impact of Hepatitis B infection—a disease that can result in long-term liver conditions like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Genevac B acts as a solution and a means to control the transmission of this serious illness, particularly in settings where the risk is high.
Brief History and Development of Genevac-B Injection
The creation of Genevac B stemmed from pioneering studies in DNA technology. It was unveiled in the latter part of the 20th century as a notable advancement in vaccine development. Since its inception, substantial efforts have been dedicated to refining its composition to bolster its effectiveness and safety measures.

Uses of Genevac-B Injection
Approved Therapeutic Uses
Genevac B is mainly employed for the prevention of Hepatitis B infection in individuals at risk of exposure to the virus. High-risk populations such as healthcare workers and babies born to mothers with HBVs, are often given vaccinations to lower the chances of infection.
Off-Label Uses
The reactivation of Hepatitis B in patients undergoing therapy is a growing concern, based on research findings indicating its preventive capabilities. In research, Genevac B is currently being studied for its potential in treatment methods and its ability to work together with other vaccines.
Composition of Genevac-B Injection
Active Ingredients
The key ingredient in the formulation of the injection is the Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). It is produced using modified yeast cells to create a refined product.
Excipients and Their Roles
The mixture contains aluminum hydroxide to boost the response. It also contains small quantities of preservatives and stabilizers to keep the vaccine effective.
Formulation Details
Genevac B is provided in a filled vial as a sterile suspension to make it easy to use and meet rigorous sterility requirements.
How Genevac-B Injection Works
Mechanism of Action
The vaccine works by introducing HB antigen into the body, which triggers the immune system to create antibodies that offer protection against exposure to the Hepatitis B virus.
Role of the Immune Response in Hepatitis B Prevention
By mimicking an infection process in the body, Genevac B treatment helps the immune system to quickly identify and combat the Hepatitis B virus to stop the infection from taking hold.
Duration of Immunity After Vaccination
Typically immunity lasts for years; in situations additional doses are advised to maintain protection over time.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosing Schedule
The standard regimen involves three doses administered at 0, 1, and 6 months. This schedule ensures optimal immunogenicity and long-lasting protection.
Primary Immunization Schedule for Adults and Children
Adults should receive a sequence of three vaccinations. Starting vaccinations, for infants, at birth is advised for all children.
Booster Doses and Recommendations
Booster shots are usually not needed for people who are in health but might be recommended for those with a higher risk or compromised immune systems.
Route and Method of Administration
The vaccine is usually given in the muscles of the arm for adults and in the thigh area for infants.
Adjustments for Special Populations
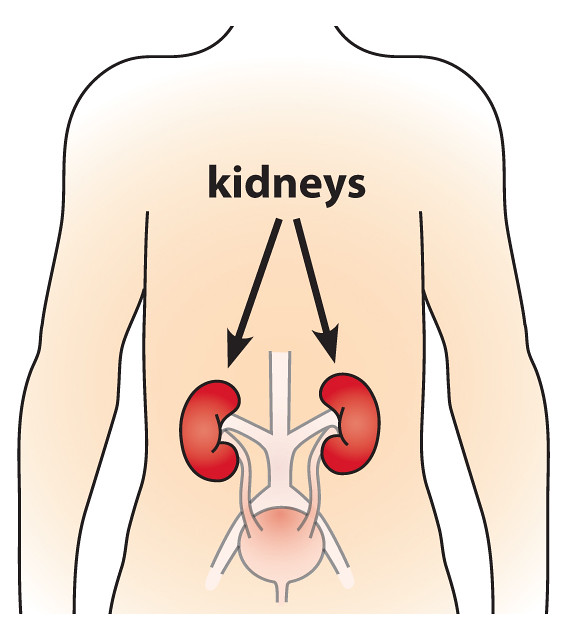
Individuals with kidney problems or those receiving dialysis may need to have their medication doses adjusted.
Storage and Handling of Genevac-B Injection
Recommended Storage Conditions
Genevac B should be kept in a temperature range of 2°C to 8°C to ensure the vaccine remains effective. It's important to prevent freezing for results.
Guidelines for Safe Transportation
Proper procedures for maintaining temperatures should be adhered to when transporting goods to avoid temperature changes along the way.
Stability and Shelf-Life Considerations
The vaccine can remain effective for long, as two years if stored properly according to guidelines.
Side Effects of Genevac-B Injection
Overview of Potential Side Effects
Genevac B is usually well received by people without causing side effects; any adverse reactions tend to be minor and temporary.
Common Side Effects
- Discomfort When Injected: Many people often experience brief pain in the area of injection.
- After getting the vaccine, a few people might have a fever.
- Feeling tired or worn out might be experienced by a person.
Rare and Serious Side Effects
- Allergies; Serious allergic reactions are very uncommon. It should be addressed promptly by professionals.
- Neurological issues: Some instances of nerve problems have been. It is uncertain if they are directly linked.
Precautions and Warnings
Important Precautions Before Administration
Administering Genevac-B Injection requires adherence to stringent protocols to ensure safety. Healthcare providers must evaluate the patient's medical history comprehensively, focusing on past reactions to vaccines and underlying health conditions. Patients should be counseled about the potential outcomes and advised on post-vaccination care.
Situations Requiring Special Attention
In situations, it's important to be extra cautious.
- Individuals with weakened systems, like those receiving chemotherapy or living with HIV/AIDS, may not respond effectively to the vaccine.
- People with long-term health issues such as diabetes or kidney problems, might need customized vaccination plans to ensure they are as effective and safe as possible.
Warning Signs to Monitor Post-Vaccination
After getting Genevac B injections or treatment, with it; people receiving it should be monitored for any reactions or side effects to ensure their safety and well-being. Continuous high temperature Severe allergies can cause swelling. Make it hard to breathe. Any unusual neurological symptoms should be reported away.
Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
Genevac B Injection should not be used in situations. If a person is allergic to any of the ingredients in the vaccine, they should steer clear of it due to their known hypersensitivity to vaccine components. Individuals who have experienced reactions after receiving a previous dose should not be given any further doses in the future to avoid any risks or complications.
Relative Contraindications and Considerations
In certain circumstances, the vaccine should be administered with caution:
- Acute febrile illnesses may temporarily delay vaccination.
- Pregnancy is not an absolute contraindication, but risks and benefits must be evaluated.
Interactions with Other Medications or Vaccines
Potential Drug Interactions
Genevac B could have an impact on the effectiveness of vaccines when taken with medications that suppress the system, like corticosteroids and chemotherapy drugs; hence, vaccination should be approached with caution in such cases.
Safety of Co-Administration with Other Vaccines
It's typically safe to get vaccines, like flu or tetanus shots; just make sure they're given in different spots to prevent any reactions, at the injection site.
Impact of Concurrent Immunosuppressive Therapy
Patients undergoing treatments that suppress their system might not respond optimally to vaccines initially; delays by vaccine administration until after reducing immunosuppression levels can improve its efficacy.
Administration to Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Individuals
As people grow older, their immune system tends to weaken, making it necessary to consider adjusting medication dosages or using levels of antigens to ensure immunity.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
From the information far, it seems that Genevac B is considered safe for use during pregnancy based on limited data findings. Moreover breastfeeding mothers can opt to receive the vaccine without concern, for their infants since the vaccine components do not pass through breast milk to the baby.

Administration to Children
Genevac B is included in the vaccination plan, for children. It is administered to newborns initially and then given in doses to provide strong immunity against diseases.
Careful Administration Guidelines
Recommendations for Safe Administration Practices
In order to guarantee safety and effectiveness in healthcare settings, it is advisable for experts to check the expiry date of the vaccine. Remember to follow procedures to avoid any contamination issues.
Avoidance of Cross-Contamination
Each needle and container should only be used once to avoid mixing substances and the risk of spreading germs and diseases.
Proper Techniques for Vaccine Injection
It is typically suggested to administer the vaccine through an intramuscular injection route. Adults usually receive it in the deltoid muscle area and infants, in the thigh region.
Overdosage and Management
Signs and Symptoms of Vaccine Overdosage
On occasion but infrequently seen is the potential for an overdose to present as: There were reactions around the area where the injection was given. Symptoms that affect the body, such as a fever or feeling unwell.
Recommended Management and Interventions
In managing the situation it's important to focus on treating the symptoms and providing care to address any systemic reactions promptly.
Handling Precautions
Proper Disposal of Used Vials and Syringes
Proper disposal procedures include following biohazard protocols, where one should place used vials and syringes in puncture proof sharps containers to avoid any injuries.
Training Requirements for Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals should receive training on how to store vaccines and administer them to ensure that safety standards are met.
Prevention of Accidental Exposure During Handling
To reduce the chance of exposure to the vaccine or bloodborne pathogens

Genevac-B Injection FAQ
What is genevac B?
Genevac B Vaccine falls under the category of medications known as 'immunizing agents', which are mainly utilized to guard against hepatitis B infection.
How to give GeneVac-b vaccine?
The GeneVac B Adult Vaccine should be administered via a muscle injection promptly following exposure to a threat to prevent infection effectively.
What type of vaccine is Genevac B?
'biologics vaccines' or 'immunizing agents'
How long does Genevac B last?
Genevac B Paediatric Injection provides a safeguard against the hepatitis B virus for a period of 3 to 5 months.
What is Genevac B vaccine?
Genevac B Vaccine is classified under the category of medications known as 'immunizing agents', which are primarily utilized for the prevention of hepatitis B infection.
Who is the manufacturer of Genevac B?
Serum Institute Of India













