Busulphan
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Busulphan
- III. How Busulphan Works
- IV. Off-Label Use
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition
- VII. Side Effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects
- IX. Interactions
- X. Warning and Contraindication
- XI. Careful Administration
- XII. Important Precautions
- XIII. Administration Specifics
- XIV. Overdosage
- XV. Storage
- XVI. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
Historical Background of Busulphan
Busulphan, also known as "busulfan," was introduced in the middle of the century as a groundbreaking chemotherapy drug. It belongs to a group of medications called alkylating agents. It has played a crucial role in transforming treatment approaches for certain types of cancers, mainly chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
Key Characteristics and General Overview
Busulphan, a compound, works by disrupting the process of DNA synthesis. Its unique chemical structure, which includes a methanesulfonate composition, allows it to have therapeutic effects that destroy cancer cells. What sets Busulphan apart is its specificity for certain types of leukemia, its longstanding use in pharmaceuticals, and its availability in both oral and intravenous forms.
II. Uses of Busulphan
Approved Indications in Cancer Therapy
Busulphan has gained recognition primarily for its effectiveness in treating myeloid leukemia (CML)12. Its specific mechanism of action on the leukemia cells has resulted in its recommendation as a first-line treatment, in medical guidelines13. Furthermore, it is also utilized for hematological disorders where suppressing the bone marrow is therapeutically advantageous124. Busulphan is a bifunctional alkylating agent with a selective immunosuppressive effect on bone marrow1.
References:
1: Busulfan: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online 2: Conditioning regimens for hematopoietic cell transplantation: one size does not fit all | Blood | American Society of Hematology 4: Busulfan, Cyclophosphamide and Melphalan As Conditioning Regimen for Pediatric Patients with AML in 1st or 2nd CR: A Retrospective Analysis from the AIEOP HSCT Registry | Blood | American Society of Hematology 3: Busulfan | Leukemia and Lymphoma Society
Therapeutic Mechanism in Bone Marrow Transplant
Before stem cell transplantation, bone marrow transplantation often involves using busulphan as a conditioning treatment. Its purpose is to eliminate the patient’s existing marrow making way for the transplantation of donor cells12. This therapeutic approach promotes the acceptance of the graft and reduces any potential complications that may arise after the transplant134. Busulphan is a myeloablative alkylating agent that prevents DNA replication through DNA crosslinking and therefore triggers cell apoptosis2.
References:
1: Q&A: Intravenous busulfan before stem cell transplant 2: Cells | Free Full-Text | Combining Mobilizing Agents with Busulfan to Enhance Hematopoietic Stem Cell Engraftment 3: Busulfan systemic exposure and its relationship with efficacy and toxicity in pediatric patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis | BMC Pediatrics | Full Text 4: Busulfan and melphalan conditioning is superior to melphalan alone in autologous stem cell transplantation for high-risk MM | Blood Advances | American Society of Hematology
III. How Busulphan Works
Pharmacodynamics and Mechanism of Action
Busulphan, a medication that alters DNA, works by causing the DNA strands to bind together. This leads to interference with DNA replication and RNA transcription, ultimately resulting in the arrest of cell division and the programmed death of cells. The specific way this medication acts highlights its effectiveness against leukemia.
Cellular and Molecular Interactions
At a level, busulphan interacts with the guanine units found in DNA. It causes molecular modifications by attaching to the N 7 position of guanine, which then leads to faulty DNA repair processes. These disruptions on a cellular level result in interference with cell division making busulphan an effective treatment against growing cancers.
IV. Off-Label Use
Alternative Therapeutic Indications
In addition to its uses, Busulphan has been used off-label in treating various blood disorders. These include; essential thrombocythemia, which is occasionally considered when other treatments are not suitable12. It is also used as a conditioning regimen for cases of thalassemia major3. Busulphan is an oral alkylating agent that reduces the production of blood cells by the bone marrow13.
References:
1: Busulfan: Dosage, Mechanism/Onset of Action, Half-Life - Medicine.com 3: Busulfan Monograph for Professionals - Drugs.com 2: Busulfan for the Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: The Mayo Clinic Experience | Blood | American Society of Hematology : Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for thalassemia major: results of a reduced-toxicity conditioning regimen based on the use of treosulfan
Research and Clinical Trials Supporting Off-label Use
Numerous research studies have revealed the potential of busulphan in therapeutic applications. For example,, clinical trials have shown its effectiveness in thalassemia patients who are undergoing bone marrow transplantation leading to promising results in terms of graft survival and disease remission123. However,, healthcare professionals must stay updated with the evidence before considering its off-label usage4. Busulphan is an alkylating agent that reduces the production of blood cells by the bone marrow and can cause serious side effects such as liver toxicity, infections, and graft-versus-host disease12.
References:
1: Pharmacokinetics of oral busulphan in children with beta thalassaemia major undergoing bone marrow transplantation | Bone Marrow Transplantation 2: Busulfan systemic exposure and its relationship with efficacy and toxicity in pediatric patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis | BMC Pediatrics | Full Text 3: BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTATION (BMT) in β-thalassaemia 4: Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Thalassemia | ASH Education Book | American Society of Hematology
V. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Recommendations
The recommended amount of busulphan usually differs depending on the reason for treatment, the age and weight of the patient well, and the specific condition being addressed. In myeloid leukemia (CML) cases, doctors commonly prescribe an oral dosage ranging from 1 to 4 mg per kilogram of body weight per day divided into several doses. However, healthcare providers must modify the dosage based on how the treatment works and any adverse side effects experienced by the patient.
Dosage Adjustments: Factors to Consider
Dosage adjustments are necessary when there is liver or kidney impairment because it affects how the drug is processed. When taking medications that can suppress bone marrow,, the dosage must be adjusted to avoid additional harmful effects. For patients, dose modifications may be needed due to changes in how their body processes the medication.
Route of Administration and Forms Available
Busulphan is available in two forms; 1. Oral tablets; These are designed for administration outside of a hospital setting. 2. Intravenous solution; This form is commonly used in situations such as bone marrow transplantation.
VI. Composition
Active Ingredient Details
The main component in busulphan is a sulfur molecule, which helps with the alkylation process. This straightforward yet effective compound ensures that the drug provides benefits.
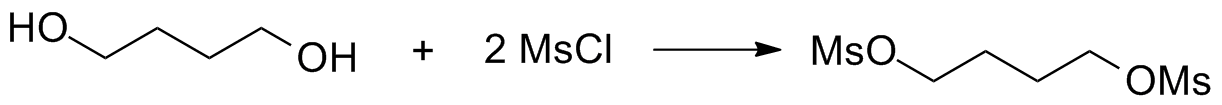
Excipients and Additional Compound Components
In addition, to the component, busulphan formulations also include certain substances that help maintain the stability and absorption of the medication. These substances may consist of stabilizers, binders, and solvents, which can differ depending on the brand and form of the drug.
VII. Side Effects
Overview of Potential Adverse Reactions
Similar to chemotherapy drugs, busulphan has its share of side effects. These can range from gastrointestinal issues to more severe suppression of bone marrow function. Additionally, long-term use may result in complications affecting the lungs, liver, and heart. It is crucial to monitor patients undergoing this treatment to ensure their well-being.
Monitoring and Reporting of Side Effects
Both doctors and patients should remain alert to side effects. It's essential to conduct blood tests, pulmonary function tests, and liver function tests. If any adverse effects occur, they should be reported promptly to the regulatory authorities, and adjustments to the dosage should be considered.
VIII. Common Side Effects
Frequency-based Listing
The side effects of busulphan can be classified based on how often they occur. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and mild leukopenia. Less common side effects include fibrosis, hepatic veno occlusive disease, and oral ulcers. Occurring side effects include cardiac complications and seizures.
Management and Mitigation Strategies
To alleviate the discomfort of nausea, it is possible to use preventive measures such as antiemetics. For severe side effects, it may be necessary to stop taking busulphan or reduce the dosage. Depending on the assessment, additional medications, like antiseizure drugs, can also be taken to counter specific side effects.
IX. Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions: Common Cofactors
Busulphans' effectiveness as a treatment can be affected by the presence of medications. One example is phenytoin, which can change how the body processes the busulphan and requires adjustments to the dosage. Other chemotherapy drugs can also potentially enhance the effects on bone marrow function.
Food and Herbal Interactions
Although there is documentation on precise food interactions, it is recommended that patients consult their healthcare provider regarding the intake of particular foods or herbal supplements while undergoing therapy. This will help ensure the therapeutic results and maintain safety.
Effects on Lab Tests and Investigations
Busulphan can potentially affect the outcomes of laboratory tests, particularly blood counts. Clinicians must be aware that there may be increases in liver enzyme levels or changes in coagulation parameters. Therefore when reviewing lab results, clinicians should exercise caution and consider the patient's prescribed treatment plan.
X. Warning and Contraindication
Absolute Contraindications
There are situations where the use of busulphan is not recommended due to increased risks. These include having known hypersensitivity to busulphan or any of its components and severe thrombocytopenia or leukopenia that cannot be attributed to the underlying disease being treated.
Relative Contraindications
Medical professionals need to use busulphan with careful consideration due to the higher likelihood of complications. If a patient already has disorders, there is an increased risk of experiencing pulmonary toxicity. Additionally, if someone has recently had or has chickenpox or herpes zoster infection, there is a potential for generalized disease.
Situational Warnings
Although busulphan has effects, it is important to recognize certain situations that require increased caution. For individuals who have previously undergone radiation or chemotherapy, there is a risk of experiencing bone marrow suppression. Additionally, if someone has a hepatic impairment, their ability to metabolize and excrete the drug may be altered, potentially increasing the risk of toxicity.
XI. Careful Administration
Administering to Special Populations
Certain groups of people require specialized treatment approaches. For example; For individuals with kidney problems, it is essential to monitor them and potentially adjust the dosage of medications. Similarly, for those with liver issues, it is crucial to carefully watch for any increased risks of side effects.
Monitoring Parameters for Safe Use
To achieve the results in therapy, it is crucial to monitor specific factors carefully; 1. Regularly check blood counts to identify potential adverse effects on bone marrow function. 2. Conduct liver function tests to monitor for any adverse effects on the liver. By monitoring these parameters, we can ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.
XII. Important Precautions
Pre-treatment Screenings and Tests
Before starting busulphan treatment, it is important to follow screening protocols. These screenings are necessary to ensure safety and maximize the effectiveness of the therapy. The essential screenings include; 1. Pulmonary Function Tests; These tests establish a baseline and help identify any existing conditions related to lung function. 2. Radiological Assessments; This step helps rule out infections or malignancies before initiating busulphan treatment. It is crucial to prioritize these screenings to provide the possible therapeutic approach for patients while maintaining their well-being, throughout the process.
Patient Counseling Points
A successful treatment plan relies not only on medications but also on well-informed patients. Important counseling topics to cover are; the side effects and how to manage them, the importance of sticking to the prescribed dosage, and follow-up appointments.
XIII. Administration Specifics
The aging population, because of changes and the presence of other health conditions, may have different responses to medications in terms of how they work and how they are processed by the body. That's why it is recommended to begin with doses when prescribing medication for this group. It is also essential to monitor for any adverse side effects.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risks and Benefits
Like many other chemotherapeutic drugs, Busulphan can potentially cause birth defects. Therefore it is generally not recommended to use it during pregnancy unless the benefits outweigh the risks. If you are a nursing mother, stop breastfeeding while undergoing this treatment.

Administration to Children: Pediatric Dosing and Safety
Children pose challenges due to their constantly changing physical conditions. Calculating medication doses based on their weight or surface area is essential to ensure that the treatment is both practical and safe. Additionally, monitoring their growth and developmental milestones is crucial to ensure they are progressing appropriately.
XIV. Overdosage
Clinical Manifestations of Overdose
An accidental or deliberate overdose can result in symptoms, including, In the short term, feeling nauseous, vomiting, and experiencing mucositis. In time, a decrease in bone marrow activity can lead to pancytopenia, a reduction in all types of blood cells.
Emergency Management and Antidote Information
In cases of overdose, it is crucial to take action. This typically involves using activated charcoal to decontaminate the system. Additionally, supportive care may be necessary, such as blood or platelet transfusions, based on the patient's needs. Although a specific antidote for busulphan is not currently available, providing supportive care remains the primary approach for treatment in these situations.
XV. Storage
Ideal Storage Conditions
To maintain the quality of the busulphan, it is essential to follow storage guidelines. Store it at a controlled room temperature away from sunlight. Also, ensure that it is kept out of reach of children to prevent any consumption.
Stability and Shelf-life
The pharmaceutical quality of busulphan remains intact for a period; When stored correctly, it can be used until the expiration date mentioned on the packaging. Disposing of unused or expired medication following the recommended guidelines is essential.
XVI. Handling Precautions
Safe Handling and Disposal Procedures
Considering the properties of busulphan, it is crucial to take necessary precautions to protect both healthcare workers and the environment. When handling or administering the drug, use equipment like disposable trays. In case of any spills, it is essential to clean them using recommended cleaning agents thoroughly. Lastly, ensure that any unused medication is disposed of through appropriate pharmaceutical waste management systems.
Personal Protective Equipment and Safety Protocol
It is crucial to prioritize one's safety when dealing with agents. Some essential steps to take include; 1. She was wearing gloves and protective gowns while preparing or administering busulphan. 2. Using masks and eye protection in situations with a risk of splashes. 3. Practicing hand hygiene after handling the substances. Remember, taking these precautions is essential to safeguard oneself during the process.
















