Amikacin
- I. Introduction to Amikacin
- II. Composition of Amikacin
- III. Uses of Amikacin
- IV. Off-label Use of Amikacin
- V. Understanding How Amikacin Works
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Amikacin
- VII. Amikacin's Interaction with Other Drugs
- VIII. Common and Rare Side Effects of Amikacin
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Amikacin Use
- X. Careful Administration of Amikacin
- XI. Special Precautions in Specific Populations
- XII. Overdose Scenarios with Amikacin
- XIII. Storage of Amikacin
- XIV. Handling Precautions for Amikacin
- XV. Importance of Patient Education
I. Introduction to Amikacin
A. Brief Overview
Amikacin is a known antibiotic, from the aminoglycoside family highly regarded for its strong ability to fight against bacterial infections. It is widely used around the world to combat infections caused mainly by gram-negative bacteria.
B. Classification and Type of Drug
Amikacin, a member of the aminoglycoside antibiotics family, exhibits an ability to kill bacteria. It is derived through semi-synthesis from kanamycin A. It Plays an essential role in today's medical treatments.
II. Composition of Amikacin
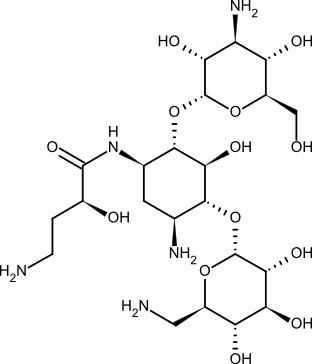
A. Chemical Structure
Amikacin has an interesting structure. It consists of a combination of sugars connected by glycosidic bonds. Amikacin is resistant to inactivation because it has a unique L ( ) γ amino α hydroxybutyryl side chain attached to its C 1 amino group.
B. Pharmaceutical Formulations
Amikacin is commonly found in pharmaceutical forms; 1. Solution; This is the most frequently used form, typically available in vials with concentrations of 50 mg/ml or 250 mg/ml. 2. Inhalable solution; Used for inhalation therapy for patients with chronic lung diseases and cystic fibrosis. 3. Ophthalmic solution; A method for delivering the medication directly to the eyes in cases of ocular infections. Each formulation serves its purpose by combating bacteria in different areas of the body, highlighting the versatility of Amikacin.
III. Uses of Amikacin
A. Approved Indications
Amikacin is an antibiotic that is effective against bacteria. It is commonly prescribed to treat severe bacterial infections. Some of the approved uses for Amikacin include treating bone and joint infections and abdominal infections (such as peritonitis) in conjunction with other medications like clindamycin, metronidazole, piperacillin/tazobactam or ampicillin/sulbactam. It can also treat meningitis and certain mycobacterial infections, including as a secondary treatment option, for tuberculosis12.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
B. Uncommon or Rare Uses
Amikacin has also found applications in atypical or infrequent scenarios, such as treating bronchiectasis and administering with ticarcillin to address granulocytopenia in individuals with cancer1.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
IV. Off-label Use of Amikacin
A. Off-label Uses in Infections
Amikacin, an antibiotic, is frequently utilized for purposes beyond its approved use. Here are a few examples of the off-label applications of Amikacin in treating infections:
- It can be an alternative in combination therapy for treating M. Avium complex (MAC) infections1.
- It effectively addresses infections caused by M. abscessus, M. Chelonae, or M. Fortuitum1.
- It proves beneficial in combating Nocardia Infections1.
Here is a reference that you can check out for more information:
B. Controversies and Potential Benefits
There has been some debate surrounding using Amikacin for off-label purposes. However, several studies have indicated that Amikacin can be beneficial in treating multidrug tuberculosis (MDR TB). Additionally, it has been employed as a therapy for sepsis treatment. Nevertheless, there are concerns regarding the adverse effects of off-label use, such as potential damage to the ears (ototoxicity) and kidneys (nephrotoxicity).
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
- Amikacin Monograph for Professionals - Drugs.com
- Amikacin: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online
- Amikacin - Wikipedia
V. Understanding How Amikacin Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Amikacin functions, in a way differentiating it from other similar medications. Being an aminoglycoside, it binds irreversibly to the ribosomes 30S subunit, obstructing the synthesis of proteins. This leads to the incapacitation and eventual demise of cells.
B. The Role of Amikacin in Treating Bacterial Infections
Amikacin plays a role in fighting against severe infections, which can be life-threatening. It targets gram bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Its ability to resist bacterial aminoglycoside modifying enzymes makes it extremely valuable in infectious disease management.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Amikacin
A. Recommended Dosage by Age and Weight
The appropriate amount of Amikacin to use relies on factors such as the patient's age, weight, and the seriousness of the infection. Both adults and children usually take a dose of 15 20 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses. However, in cases where patients are severely ill higher doses may be administered with close monitoring by a healthcare professional.
B. Methods of Administration
Amikacin is commonly given through the veins or muscles, although the method of administration might vary depending on the situation. When administered intravenously (IV), it is typically infused for 30 to 60 minutes. On the hand, when given intramuscularly (IM), it is injected into the deeper layers of muscle tissue. Inhalation is another route used for patients with lung conditions, where amikacin is delivered as a respiratory solution.
VII. Amikacin's Interaction with Other Drugs
A. Potential Drug-Drug Interactions
Like any medicine, Amikacin can interact with drugs. It's essential to be cautious when using it with ototoxic medications such as loop diuretics or cisplatin as it may increase the risk of kidney or hearing damage.
B. Precautions with Other Medications
When using Amikacin with medications, it's important to be cautious and take specific measures. Make sure you let your healthcare provider know about all the medicines you're currently taking, including, over-the-counter drugs, prescription medications, and herbal supplements. This way they can adjust the dosage if needed or keep an eye on any potential side effects ensuring the best possible treatment results.
VIII. Common and Rare Side Effects of Amikacin
A. Most Frequently Reported Side Effects
Like any medication, Amikacin can cause side effects. Reported reactions are usually not severe and might include; Kidney problems; This can be identified by increased levels of creatinine, reduced urine output, or abnormal findings in urine analysis. Ear problems; These can manifest as ringing in the ears (tinnitus), dizziness (vertigo), or even loss of hearing. Reactions at the injection site; may include pain and redness (erythema). It is swelling in a specific area.
B. Understanding Rare but Serious Side Effects
Although Amikacin has manageable side effects, it is essential to note that severe but rare complications can occur. These may include blockade, which can result in muscle weakness and potential respiratory depression. Additionally, hypersensitivity reactions such as rash, fever or even an anaphylactic reaction may occur. If any of these side effects happen, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Amikacin Use
A. Medical Conditions and Amikacin
There are situations where it's essential to be careful when considering Amikacin treatment. These include; If you have existing kidney problems, amikacin's ability to harm the kidneys can worsen your condition. If you have disorders like myasthenia gravis or Parkinson's disease, there is a risk of experiencing muscle and nerve blockage with Amikacin. Individuals with hearing issues should use Amikacin cautiously because of its potential to cause hearing problems.
B. When Amikacin Should Be Avoided
Amikacin should be avoided in patients with hypersensitivity to aminoglycosides because it can lead to severe allergic reactions. Furthermore, it is recommended to exercise caution or altogether avoid using amikacin in neonates and premature infants due to their kidney function and the potential for drug accumulation.
X. Careful Administration of Amikacin
A. Monitoring Parameters for Safe Use
To ensure the usage of Amikacin, healthcare professionals should regularly conduct the following monitoring measures; 1. Renal function assessment; This includes analyzing serum creatinine levels and conducting urinalysis to identify any indications of kidney damage. 2. Audiometric testing; during long-term treatment, it is important to periodically perform hearing tests to detect any potential harm caused by the medication. 3. Monitoring drug levels; It is essential to monitor the concentration of Amikacin in the bloodstream to prevent accumulation and potential toxicity, particularly in patients with impaired kidney function.
B. Modifying Doses Based on Patient Response
The dosage of Amikacin may need to be adjusted depending on how the patient responds and their side effect profile. For example, if the patient has reduced kidney function, it is essential to decrease the dosage to avoid drug buildup. Furthermore, if any adverse effects occur, it is recommended to stop taking the medication and begin appropriate treatment for the symptoms.
XI. Special Precautions in Specific Populations
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
Special attention should be given to patients, especially those with existing kidney problems when prescribing Amikacin. As people age, their kidney function tends to decrease, which increases the likelihood of drug buildup, kidney damage, and hearing loss. It is crucial to monitor renal function and drug levels in these patients and make necessary dosage adjustments accordingly.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Amikacin should only be used during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the risks to the developing baby. Since it can pass through the placenta, there is a possibility of causing harm to the fetus, such as hearing and kidney problems. Similarly, since Amikacin can be present in breast milk, it's essential to be cautious when giving it to breastfeeding mothers as there may be a risk to their babies.
C. Administration to Children
The careful observation of patients is crucial when using Amikacin. It is essential to adjust the dosage based on their weight and regularly monitor the drug levels in their system in newborns and infants who have underdeveloped kidneys. Additionally, it is vital to watch for any signs of hearing or kidney problems.
XII. Overdose Scenarios with Amikacin
A. Symptoms of Overdose
Taking an amount of Amikacin can result in significant complications. The symptoms of an overdose are similar to the side effects, but they tend to be more severe. These can include hearing loss, dizziness, kidney damage, difficulty breathing, and muscle paralysis caused by the neuromuscular blockade.
B. Emergency Management for Overdose
If someone accidentally takes much Amikacin, it is essential to seek immediate medical help. The usual course of action involves stopping the medication, providing care, and considering interventions like hemodialysis to eliminate the drug from the body. Addressing any accompanying symptoms, such as breathing problems or kidney issues, is crucial for the patient's well-being and recovery.
XIII. Storage of Amikacin
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
To maintain the effectiveness of Amikacin it is essential to store it. The recommended storage temperature is between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) away, from light and moisture. It is advisable to refrigerate the reconstituted solutions and use them within 24 hours.
B. Precactions for Safe Storage
It's essential to store Amikacin. Make sure to keep it from children and pets. If you have any leftover medication or waste, be sure to follow the guidelines for disposal. Please don't throw it in the trash or flush it down the drain, as that could harm the environment.
XIV. Handling Precautions for Amikacin
A. Recommendations for Safe Handling
It is crucial to handle Amikacin to avoid any accidental exposure or misuse. To ensure safety, please follow these guidelines; 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, when preparing Amikacin for administration. 2. Sterile Technique; Always use techniques during the preparation and administration of Amikacin to prevent contamination or infections. 3. Avoid Self Injection; Be cautious to prevent self-injection as it may result in potential side effects. Remember, following these precautions will help ensure the handling of Amikacin and minimize any risks associated with its use.
B. Disposal Procedures
It is crucial to handle Amikacin to avoid any environmental harm and accidental consumption by humans or animals. Any unused Amikacin, expired medication, or waste materials should be disposed of following the regulations for waste in your area. It is essential not to throw them with regular household waste or flush them down the drain.
XV. Importance of Patient Education
A. Key Points for Patients
It is crucial to provide patients with education when it comes to Amikacin therapy. Patients should be well informed about the following aspects; 1. Side Effects; They need to understand both severe side effects and know when it is necessary to seek medical attention. 2. Dosing Schedule; patients need to follow the dosage and timing strictly to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment. 3. Monitoring; Patients should comprehend why regular monitoring of function and hearing is necessary during the course of therapy.
B. Promoting Adherence to Therapy
To ensure that patients stick to their Amikacin treatment, it's crucial to educate them about how important the medications are for treating their infection. They should be made aware of the consequences if they don't adhere to the prescribed regimen and be provided with ways to manage any side effects. Regular checkups and supportive care can also help increase compliance. The role of pharmacists and healthcare providers in providing this education and support is vital.
Amikacin FAQ
- What are the side effects of Amikacin?
- What class does Amikacin belong to?
- What is Amikacin injection used for?
- How is Amikacin dosing determined?
- What is the typical dosage for Amikacin?
- What is Amikacin inhalation used for?
- What is the brand name for Amikacin?
- How is Amikacin for inhalation administered?
- What is Amikacin Sulfate?
- Is Amikacin an antibiotic?
- Is Amikacin safe for dogs?
- What is the coverage of Amikacin?
- What is an Amikacin trough level?
- How is Amikacin administered via a nebulizer?
- What is the mechanism of action of Amikacin?
- What is the cost of Amikacin?
- What is Amikacin Liposome Inhalation Suspension?
- Is Amikacin used for urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
- What is an Amikacin package insert?
- What does Amikacin level refer to?
- What are the dosing guidelines for Amikacin?
- What is an Amikacin nomogram?
- How is Amikacin IV administered?
- Can Amikacin be used for horses?
- What are the uses of Amikacin?
- Is there an oral form of Amikacin?
- What are the contraindications for Amikacin?
- Does Amikacin come in a tablet form?
- What is an Amikacin dosing calculator?
- What are Amikacin peak and trough levels?
- What is Amikacin sulfate injection used for?
- What is Amikacin ototoxicity?
- What is Amikacin medication?
- Is Amikacin injection used for dogs?
- What is an Amikacin trough level?
- What are the adverse effects of Amikacin?
- Is Amikacin an aminoglycoside?
- Are there Amikacin eye drops?
- What is the Amikacin peak level?
- What is the Amikacin single daily dose?
- What is liposomal Amikacin?
- How does Amikacin compare to Gentamicin?
- What are other names for Amikacin?
- What is the classification of Amikacin?
- What is an Amikacin calculator?
- What are the warnings associated with Amikacin?
- What is the route of administration for Amikacin?
- What are the uses of Amikacin injection?
- What are Amikacin interactions?
- What is the trade name of Amikacin?
- What is Amikacin toxicity?
- What antibiotic class does Amikacin belong to?
- What are the side effects of Amikacin in dogs?
- What is the structure of Amikacin?
- What is Amikacin bladder irrigation?
- Is Amikacin effective against Pseudomonas?
- What is Amikacin nephrotoxicity?
- Can Amikacin cause hearing loss?
- What is Amikacin infusion?
- What is the Amikacin inhalation dose?
- What is Amikacin nebulizer solution?
- What is the Amikacin nebulizer dose?
- Is Amikacin effective against gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria?
- What is Amikacin's veterinary use?
- What is an Amikacin vial?
- What does Amikacin monitoring involve?
- What is the price of Amikacin injection?
- What is the spectrum of Amikacin?
- What is the spectrum of activity of Amikacin?
- Are there Amikacin ear drops?
- What is Amikacin extended interval dosing?
- What is the protocol for Amikacin dosing?
- What is Amikacin dilution?
- What is the brand name of Amikacin?
- What is the price of Amikacin?
- What is the Amikacin protocol for dogs?
- When is the peak level timing for Amikacin?
- What is the generic name for Amikacin?
- Can Amikacin be used topically?
- Is Amikacin used for MAC (Mycobacterium Avium Complex)?
- What is the relationship between Amikacin and Dexamethasone?
- What are the side effects of Amikacin when administered through a nebulizer?
- Is Amikacin effective for Pseudomonas?
- How is Amikacin administered?
- Does Amikacin need to be refrigerated?
- What does Amikacin cover?
- Is Amikacin an antibiotic?
- Why is Amikacin contraindicated in renal failure?
- Why is Amikacin given once daily?
- How long does it take for Amikacin to work?
- How long does Amikacin stay in your system?
- How does Amikacin work?
- How is Amikacin injection diluted?
- How is the Amikacin dose calculated?
- What is Amikacin in urine culture?
- When should Amikacin levels be taken?
- Is Amikacin a strong antibiotic?
- To which group does Amikacin belong?
- Can Amikacin cause hearing loss?
- Can Amikacin be given orally?
- Can Amikacin be given IM (Intramuscular)?
- Can Amikacin be given IV push?
- How is Amikacin administered?
- What is Amikacin used to treat?
- How much does Amikacin cost?
- What does Amikacin treat?