Nitroglycerin Patch
- I. Introduction to Nitroglycerin Patches
- II. Composition of Nitroglycerin Patches
- III. How Nitroglycerin Patches Work
- IV. Uses of Nitroglycerin Patches
- V. Off-Label Uses of Nitroglycerin Patches
- Nitroglycerin patches for Tendonitis
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Common Side Effects of Nitroglycerin Patches
- VIII. Serious Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- IX. Interactions with Other Medications
- X. Warnings and Contraindications
- XI. Special Precautions in Administration
- XII. Handling and Storage of Nitroglycerin Patches
- Cutting nitroglycerin patches
- XIII. What to Do in Case of Overdosage
- XIV. Important Precautions for Handling Nitroglycerin Patches
I. Introduction to Nitroglycerin Patches
Overview of nitroglycerin as a medication
Nitroglycerin, a vasodilator, has played a vital role in treating heart conditions with medications for more than a hundred years. Its main function is to relieve chest discomfort and enhance blood circulation to the heart muscle.
Historical context and development of the patch form
Nitroglycerin's medical application originated in the 1800s, and its introduction in patch form proved to be a significant advancement in the 20th century. This innovation offered a means of administering uniform doses of the drug through the skin, leading to alleviation of angina symptoms.
II. Composition of Nitroglycerin Patches
Active ingredients
The main ingredient found in these patches is nitroglycerin. It is carefully adjusted to guarantee absorption into the skin, releasing a regulated dose of medication for a set duration.
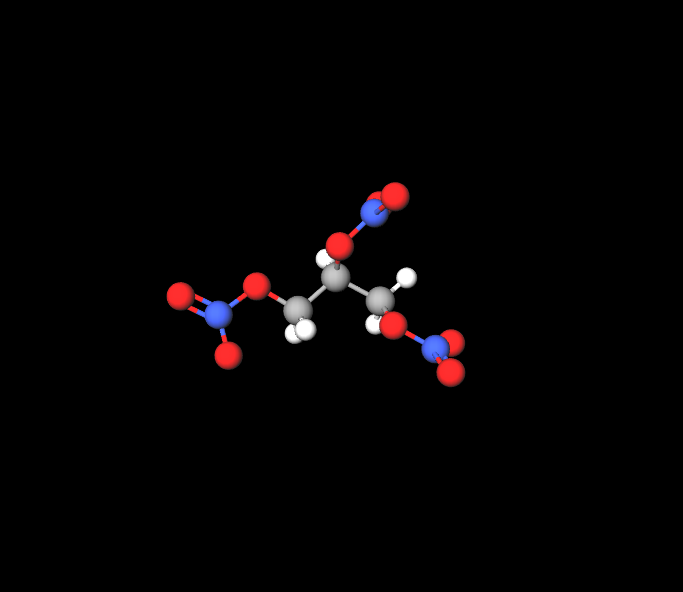
Inactive ingredients and their functions
- Adhesive substances: Help the patch stick to the skin smoothly without causing any irritation.
- Enhancers for penetration; Boost the drugs capacity to enter the skin.
- Stabilizing agents: Preserve the effectiveness and strength of the ingredient in different environmental settings.
III. How Nitroglycerin Patches Work
Mechanism of action in the body
Nitroglycerin patches work by releasing nitroglycerin into the skin, which then gets into the bloodstream. After absorption, it changes into nitric oxide, causing relaxation of the muscles, in blood vessels, and widening of arteries and veins.
The role of nitroglycerin in vasodilation
The widening of blood vessels leads to pressure on the heart before and after contraction, reducing the need for oxygen in the heart muscle and easing chest pain. These functions highlight its importance in caring for the heart.
IV. Uses of Nitroglycerin Patches
Primary indications: Angina pectoris
Nitroglycerin transdermal patches are primarily used to prevent episodes of angina (chest pain) in people who have coronary artery disease (narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart). These patches can only be used to prevent attacks of angina; they cannot be used to treat an attack of angina once it has begun. Nitroglycerin belongs to a class of medications called vasodilators. It works by relaxing the blood vessels, reducing the workload on the heart, and consequently decreasing the need for oxygen by the heart muscle1
V. Off-Label Uses of Nitroglycerin Patches
Exploring non-standard applications in medical practice
Nitroglycerin patches, although primarily intended for treating angina, have found unconventional applications in various medical contexts. When traditional treatments prove insufficient, healthcare professionals may recommend the use of nitroglycerin patches for the following purposes:
-
Heart Failure: Nitroglycerin patches can help manage heart failure by promoting blood flow and reducing the workload on the heart. By relaxing blood vessels, they decrease the amount of work the heart has to do14.
-
Esophageal Spasms: These patches may also be beneficial in alleviating esophageal spasms. By relaxing the smooth muscle within blood vessels, nitroglycerin facilitates vasodilation, which can help ease spasms and improve blood flow21.
Nitroglycerin patches for Tendonitis
Evidence supporting off-label use
Recent studies have started to back up these applications, but more research is required to grasp their effectiveness and safety in these situations fully.
VI. Dosage and Administration
Proper application of the patch
To ensure the patch works well, it should be placed on a dry and hair-free area of the skin. Usually, it is positioned on the chest or back for absorption.
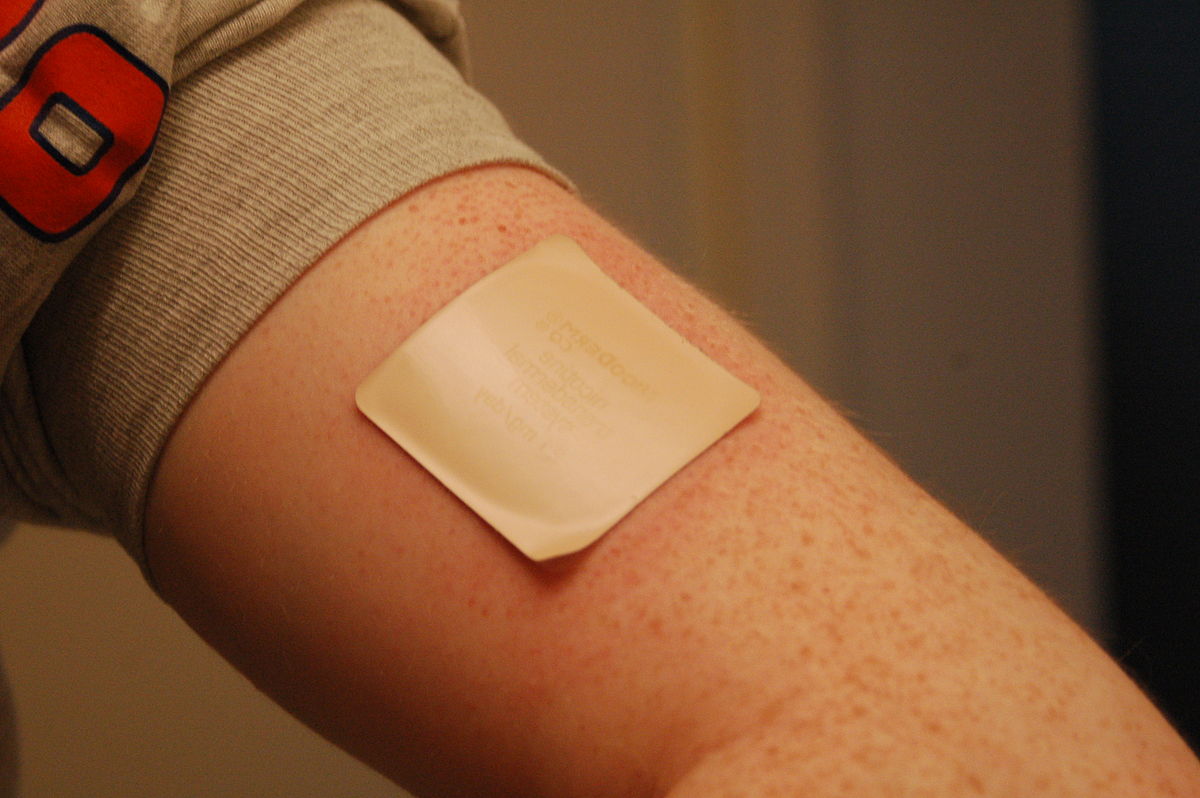
Dosage guidelines and duration of use
The amount of nitroglycerin patches needed differs depending on the patient's requirements. Usually, a patch is worn for 12 to 14 hours, followed by a break without a patch to avoid developing tolerance.
VII. Common Side Effects of Nitroglycerin Patches
List of frequent side effects
- Frequent headaches can be caused by the widening of blood vessels.
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded may occur when getting up quickly from sitting or lying down.
- It is also common to experience skin irritation where the product is applied.
Management of side effects
Most of the side effects can typically be controlled using pain relievers available without a prescription, ensuring proper hydration and repositioning the patch to alleviate any skin discomfort. If the side effects continue, seeking advice from a healthcare professional is recommended.
VIII. Serious Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Identifying Severe Reactions
Although nitroglycerin patches are typically considered safe, in some instances, they may lead to serious adverse effects. Signs like low blood pressure, sudden collapse, and intense dizziness signal critical situations that require prompt medical attention.
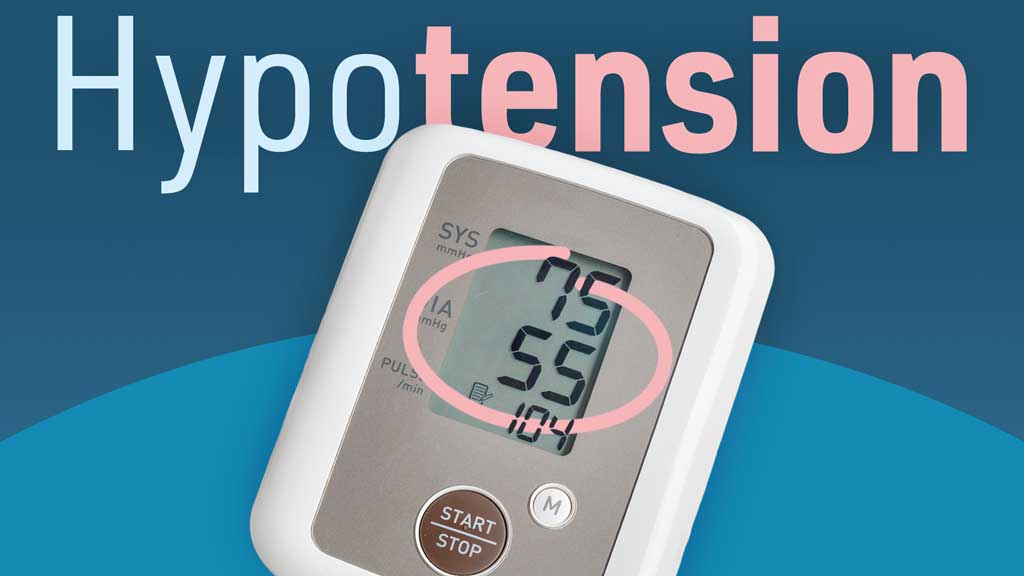
When to Seek Medical Help
If you start having allergic reactions like trouble breathing swelling in your face, lips, tongue or throat it's crucial to seek medical help right away. Also if you're dealing with headaches, blurry vision or a dry mouth it's important to reach out to a healthcare professional, for advice.
IX. Interactions with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions
When phosphodiesterase inhibitors are taken together, it may lead to a drop in blood pressure.
- The use of medications can strengthen blood pressure by lowering the impact of nitroglycerin.
- Taking aspirin could elevate nitroglycerin levels in the bloodstream, possibly intensifying its benefits and drawbacks.
Impact on Efficacy and Safety
When nitroglycerin is taken with medications, it can either reduce its effectiveness or worsen its side effects. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of all the medications they are currently taking to prevent any interactions that may affect the success or safety of the treatment.
X. Warnings and Contraindications
Specific Health Conditions That Contraindicate Use
Patients with anemia, elevated intracranial pressure, or recent heart attacks, should avoid using nitroglycerin patches. These individuals may experience worsened symptoms and complications if they use the medication.
Situations Requiring Caution
It's important to be cautious when using this medication if you have glaucoma, hypothyroidism, or severe liver disease. Make sure to have checkups with your healthcare provider while undergoing treatment.
XI. Special Precautions in Administration
Administration to Elderly Patients
Older individuals could potentially experience sensitivity to the blood pressure-lowering impact of nitroglycerin, necessitating modifications in doses and careful observation for symptoms of lightheadedness and the risk of falling.
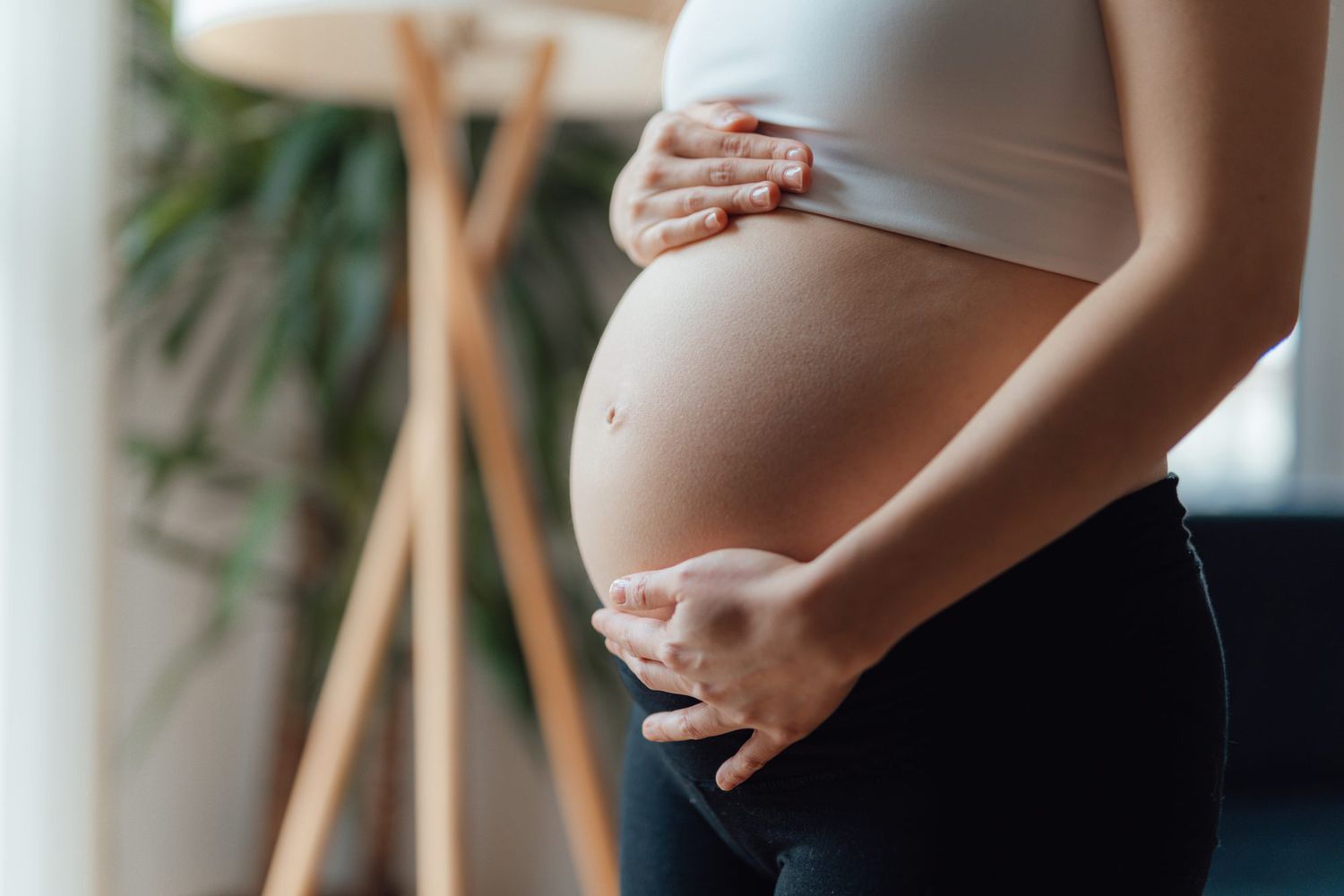
Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Nitroglycerin falls into pregnancy category C so it should only be taken if necessary and after a healthcare professional has evaluated the risks and benefits. Its safety during breastfeeding is uncertain, so it's important to be cautious.

Considerations for Administering to Children
Where research exists on the use of nitroglycerin patches in children, it is advisable to reserve their use for critical situations and ensure close medical monitoring.
XII. Handling and Storage of Nitroglycerin Patches
Recommended Storage Conditions
For effectiveness, patches should be kept in a dry place at room temperature, shielded from light and moisture. For best results, store them within the range of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
Disposal of Used Patches
Remember to fold patches in half with the adhesive sides touching each other before properly disposing of them to avoid any accidental contact or ingestion, by kids or pets.
Cutting nitroglycerin patches
Avoid attempting to trim or alter the patch to modify the dosage. Consult your physician if you feel that the medication is not functioning as expected. Place the patch on a dry skin area with minimal or no hair, and ensure it is free of scars, cuts, or irritation.
XIII. What to Do in Case of Overdosage
Symptoms of Overdose
Experiencing an intense headache along with feelings of confusion and fever could be accompanied by either a rapid or slow heart rate.
Immediate Actions and Antidotes
In case of an overdose, the initial measure is to take off the patch. It's crucial to seek medical assistance right away. Treatment involves addressing symptoms and providing support, such as administering fluids and raising the limbs to address low blood pressure.
XIV. Important Precautions for Handling Nitroglycerin Patches
Safety Tips During Application and Removal
It's important to wash your hands before and after putting on or taking off a patch to avoid accidentally coming into contact, with the medication.
Avoiding Contamination and Ensuring Efficacy
Before applying the patch, it's important to ensure that its integrity remains intact. Avoid cutting, modifying, or subjecting the patch to temperatures, as these actions could impact the medication's effectiveness.