Noradrenaline
- I. Introduction: An Overview of Noradrenaline
- II. Composition: Breaking Down the Chemical Structure
- III. How It Works: The Mechanism of Action
- IV. Uses: Medical Applications of Noradrenaline
- V. Off-label Uses: Expanding Beyond the Norm
- VI. Dosage and Administration: Guidelines for Use
- VII. Side Effects: Understanding the Risks
- VIII. Common Side Effects: What to Expect
- IX. Interactions: What You Should Know
- X. Warnings: Vital Cautions for Use
- XI. Contraindications: When to Avoid Noradrenaline
- XII. Careful Administration: Special Cases
- XIII. Important Precautions: Safeguarding Health
- XIV. Administration to Elderly: Age-Specific Guidelines
- XV. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- XVI. Administration to Children: Pediatric Usage
- XVII. Overdosage: What Happens and How to Manage
- XVIII. Handling Precautions: Safe Storage and Disposal
- XIX. Summary and Conclusion
I. Introduction: An Overview of Noradrenaline
Brief History of Noradrenaline
The origins of noradrenaline can be traced back to the 1900s when scientists first isolated it as part of their efforts to study the workings of the sympathetic nervous system. As a type of catecholamine derived from acids, this neurotransmitter has captured significant interest in both neurobiology and clinical medicine.
General Uses in Medical Science
Managing blood pressure Dealing with cardiogenic shock Handling allergic reactions Noradrenaline is crucial in critical care situations as it quickly stabilizes the patient's hemodynamics.
Importance in Neurotransmission
Noradrenaline isn't just commonly found in emergency rooms; it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain. It helps regulate cognitive functions such, as attention, alertness, and memory consolidation.
II. Composition: Breaking Down the Chemical Structure
Molecular Formula and Weight
Noradrenaline, which has a formula of C8H11NO3 and a molecular weight of 169.18 g/mol, is a relatively uncomplicated substance, with significant physiological effects.
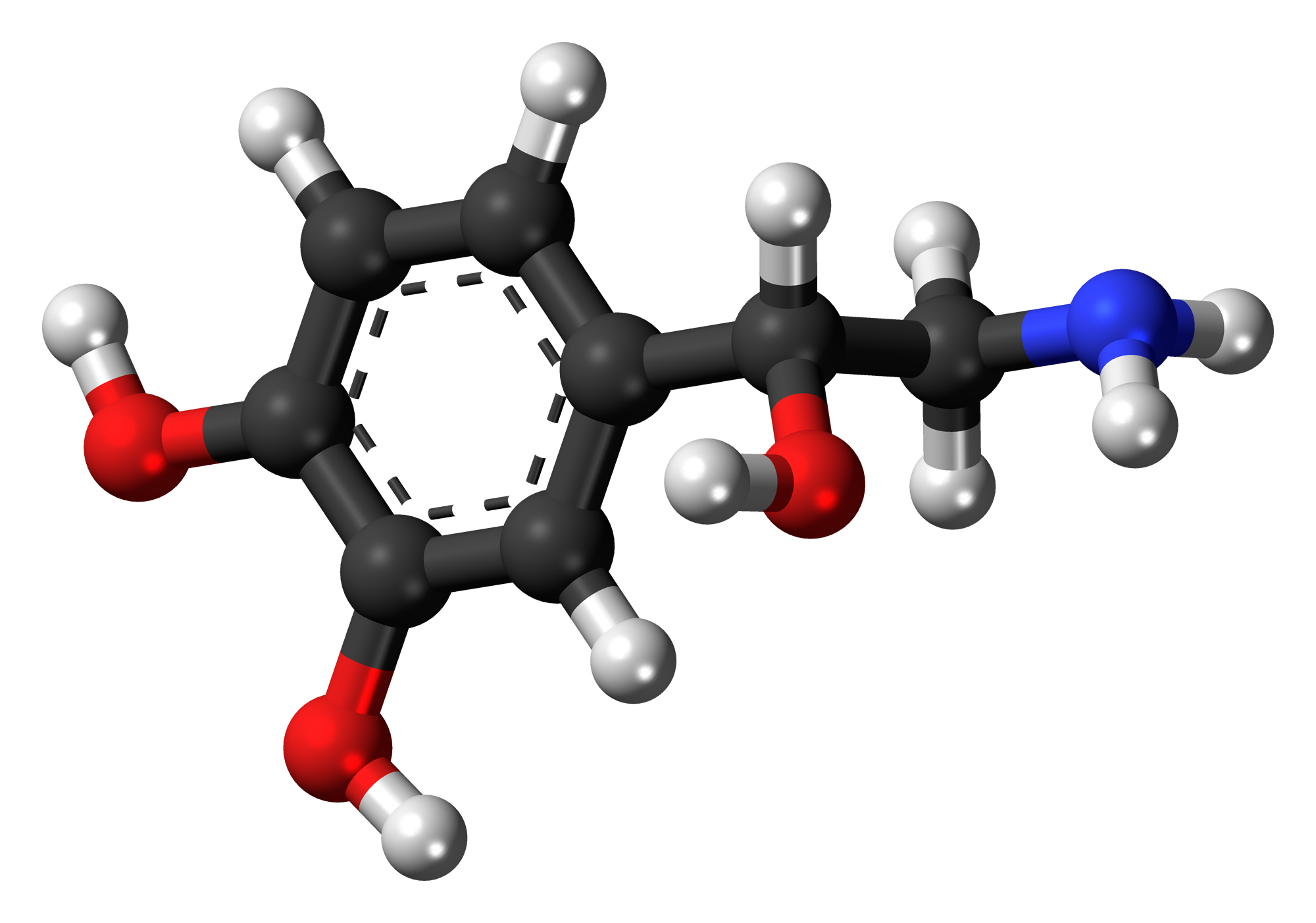
Physiochemical Properties
It's a molecule that loves water and usually remains stable in environments. However, it can be easily oxidized; It requires careful storage.
Chemical Classifications
Noradrenaline is categorized as a catecholamine along with neurotransmitters such, as dopamine and epinephrine, all falling under the phenethylamines class.
III. How It Works: The Mechanism of Action
Role as a Neurotransmitter
Noradrenaline functioning as a neurotransmitter plays a role in regulating plasticity and enhancing cognitive sharpness. It is produced in the locus coeruleus and then distributed through axon pathways.
Vasoconstrictive Effects
Noradrenaline works effectively as a vasoconstrictor, helping to improve circulation by narrowing the peripheral blood vessels. This action leads to an increase in both blood pressure and cardiac output.
Receptor Binding and Activation
The main focus of the drug is on alpha receptors. When it binds to these receptors, it triggers a series of actions, within the cells that enhance its neurotransmitter effects.
IV. Uses: Medical Applications of Noradrenaline
Treatment of Hypotension
Noradrenaline, also known as norepinephrine, is a hormone and neurotransmitter that plays an important role in the body’s “fight-or-flight” response. It is used as a medication to increase and maintain blood pressure in limited, short-term serious health situations 1. Noradrenaline is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure 2. It is also used to treat life-threatening low blood pressure (hypotension) that can occur with certain medical conditions or surgical procedures 3. Noradrenaline acts as a stress hormone and is widely used as a vasoactive agent that narrows blood vessels and increases blood pressure. It’s responsible for making your heart rate and blood pressure increase during the body’s natural fight or flight response 4.
1: Cleveland Clinic 3: Drugs.com 2: Wikipedia 4: Dr. Axe
Cardiogenic Shock Management
Cardiogenic shock is a medical emergency that occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. In such situations, it is essential to ensure that the heart receives sufficient blood flow and that organs receive enough oxygen. Vasopressors and inotropes are commonly used to treat cardiogenic shock 1. Noradrenaline, also known as norepinephrine, is a vasoactive agent that is widely used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock 2. It helps to increase blood pressure and cardiac output by constricting blood vessels and increasing heart rate 2.
Anaphylactic Reactions
Epinephrine and noradrenaline are two hormones that are used in the treatment of anaphylaxis. Epinephrine is the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis, and it is administered via injection1. On the other hand, Noradrenaline is not used as a first-line treatment for anaphylaxis. It is used in situations where epinephrine is unavailable or ineffective2.
Here are some references that provide more information about epinephrine and noradrenaline:
- WebMD provides a detailed comparison between epinephrine and noradrenaline, including their medical uses and effects on the body.
- Medical News Today explains the differences between epinephrine and noradrenaline, their functions, and their medical uses.
- Healthline provides a comprehensive overview of epinephrine and noradrenaline, including their main differences, uses, and more.
V. Off-label Uses: Expanding Beyond the Norm
As an Antidepressant Agent
According to a research article published in BMC Psychiatry, the French Association for Biological Psychiatry and Neuropsychopharmacology and the foundation FondaMental developed expert consensus guidelines for managing treatment-resistant depression 1. The guidelines combine scientific evidence and expert clinicians’ opinions to produce recommendations for treatment-resistant depression. The guidelines provide guidance for successive antidepressant pharmacological treatments for non-responders in significant depression 1.
Although it has not been explicitly stated, there is some potential in using noradrenaline as a treatment for treatment-resistant depression 1.
Cognitive Function Enhancement
According to a research article published in Brain, noradrenaline is a crucial neuromodulator that controls brain states, vigilance, action, reward, learning, and memory processes 12. A meta-analysis of 10 studies (1300 patients) showed a significant small positive effect of noradrenergic drugs on global cognition, measured using the Mini-Mental State Examination or Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale—Cognitive Subscale 3.
Although studies suggest that cognitive enhancement could have some advantages, further confirmation is needed through extensive clinical trials 1.
Experimental Uses in Psychiatry
According to a research article published in Brain, noradrenaline is a crucial neuromodulator that controls brain states, vigilance, action, reward, learning, and memory processes 12. A review article published in Frontiers in Psychiatry suggests that atomoxetine, a selective norepinephrine (NE) reuptake inhibitor, was approved for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) treatment in children, adolescents, and adults 3. The article also mentions that a series of studies have been published suggesting that atomoxetine is effective in treating ADHD symptoms for children with various types of comorbidity 3.
A study published in Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience suggests that dopamine and noradrenaline signaling and function in the CNS may act in parallel and overlapping manner 4.
Although studies suggest that cognitive enhancement could have some advantages, further confirmation is needed through extensive clinical trials 1.
VI. Dosage and Administration: Guidelines for Use
Standard Dosage for Various Conditions
The prescribed doses can differ significantly depending on the medical situation. Typically, the recommended dosage for administration ranges from 0.01 to 0.3 mcg/kg/min.
Route of Administration
The gold standard for administering medication is through means, especially when immediate needs require its use.
Dosage Adjustments and Individualization
Adjusting the dosage may be necessary in cases such as when a patient has kidney problems or is older.
VII. Side Effects: Understanding the Risks
Cardiovascular Complications
These conditions can involve heart muscle damage and irregular heart rhythms, which need observation.
Neurological Effects
Although it is uncommon, there can be instances where individuals experience neurological effects such as restlessness and involuntary shaking.
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
Episodes of feeling sick to the stomach, or throwing up occur often, but they happen occasionally.
VIII. Common Side Effects: What to Expect
Palpitations
It is not unusual for patients to sometimes feel palpitations. These sensations often go away when the dosage is reduced.
Anxiety or Nervousness
Sometimes, people experience moments of increased anxiety or nervousness. It usually doesn't last long.
Elevated Blood Pressure
Blood pressure increases result from pharmacological effects, although it requires careful monitoring.
IX. Interactions: What You Should Know
Drug-Drug Interactions
Using MAOIs, tricyclic antidepressants, or other vasopressors simultaneously can potentially lead to crises.
Drug-Food Interactions
The impact of alcohol on noradrenaline can vary from person to person, either enhancing or reducing its effects based on metabolism.
Lab Test Interactions
Caution should be exercised when interpreting assays that measure catecholamines, as the presence of noradrenaline can potentially interfere with the results.
X. Warnings: Vital Cautions for Use
Risk of Tachyphylaxis
Tachyphylaxis, which refers to a decrease in response, to doses, can happen with Noradrenaline. It is crucial to monitor the effectiveness of the medication to ensure its desired effects.
Contraindications in Certain Conditions
Severe high blood pressure Overactive thyroid Adrenal gland tumor causing blood pressure and other symptoms Having clear guidelines, on what not to do helps prevent adverse effects.
Safety Precautions
It is essential to follow the established guidelines, for administering medication and ensure that emergency medical equipment is readily available.
XI. Contraindications: When to Avoid Noradrenaline
Severe Hypertension
Patients with uncontrolled blood pressure should avoid using Noradrenaline because it increases the risk of hypertensive emergencies.
Hyperthyroidism
The use of noradrenaline is not recommended as it can worsen the symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
Pheochromocytoma
This medication is not recommended for individuals with pheochromocytoma because it can enhance the release of catecholamines which could be problematic.
XII. Careful Administration: Special Cases
Renal Impairment
It is recommended to adjust the dosage, in patients with kidney problems.
Hepatic Impairment
It is wise to keep track of liver enzymes and make dose adjustments if needed.
Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases
Exercise caution when administering noradrenaline to patients who are prone to arrhythmias or have ischemic heart conditions.
XIII. Important Precautions: Safeguarding Health
Monitoring Blood Pressure
It is crucial to monitor the hemodynamics while administering Noradrenaline.
Administering with Care in Elderly
Elderly individuals might need doses of medication and more regular checkups because their bodies have decreased resilience.
Safety Measures for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers need to follow aseptic procedures to prevent any chance of contamination.
XIV. Administration to Elderly: Age-Specific Guidelines
Lower Dosage Requirements
In some cases, a lower dose is often enough to reach the desired treatment outcomes in older individuals.
Monitoring for Cognitive Changes
It's essential to monitor function because changes in metabolism that come with age can cause drug effects to be different than expected.
Risk of Falls
It is recommended to stay alert and cautious about the possibility of experiencing changes in blood pressure when standing up, as it can increase the risk of falling.
XV. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Fetal Considerations
Animal studies have indicated harmful effects, on fetal development, so it is crucial to thoroughly assess the use of this substance during pregnancy.
Lactation Concerns
Although there is data available, it is advisable to exercise caution when giving this medication to breastfeeding mothers.
Alternative Treatments
It might be worth considering treatment options in the field of pharmacotherapy.
XVI. Administration to Children: Pediatric Usage
Age-Specific Dosages
There is still a need to determine dosages conclusively, and they should be tailored to each individual.
Safety Profile in Pediatrics
Although it is usually considered safe it is essential to monitor pediatric physiology due, to its delicate nature.
Clinical Studies on Effectiveness
There is literature available, on pediatric applications, but it is gradually increasing.
XVII. Overdosage: What Happens and How to Manage
Symptoms of Overdosage
Some possible signs of this condition could be blood pressure, rapid heart rate, and potentially irregular heart rhythms.

Emergency Management
The critical components of management involve promptly stopping the medication and providing symptomatic treatment.
Long-term Effects
If immediate action is taken, long-term complications are usually not seen.
XVIII. Handling Precautions: Safe Storage and Disposal
Optimal Storage Conditions
Keep Noradrenaline stored in a dark location, usually at temperatures ranging from 2 to 8 degrees Celsius, to ensure its effectiveness in pharmacology.
Shelf Life
Check the expiration date mentioned on the package to ensure that the product is still within its period.
Proper Disposal Methods
Dispose of unused medication following local pharmaceutical waste management guidelines to reduce the environmental impact.
XIX. Summary and Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Noradrenaline is a type of catecholamine that has various medical uses. It has contraindications and needs careful administration. When dealing with populations like the elderly, children, and pregnant or nursing women, customized approaches are necessary.
Final Recommendations for Safe and Effective Use
It is always essential to seek guidance from healthcare professionals to receive a treatment plan. Additionally, make sure to follow the prescribed dosages and guidelines for administration.
Encouragement for Further Reading and Consultation
To understand Noradrenaline and its uses, it is highly recommended to read medical research papers and consult with healthcare professionals.